The End of the Carolingian Civil War …
Years: 843 - 843
August
The End of the Carolingian Civil War and the Treaty of Verdun (843)
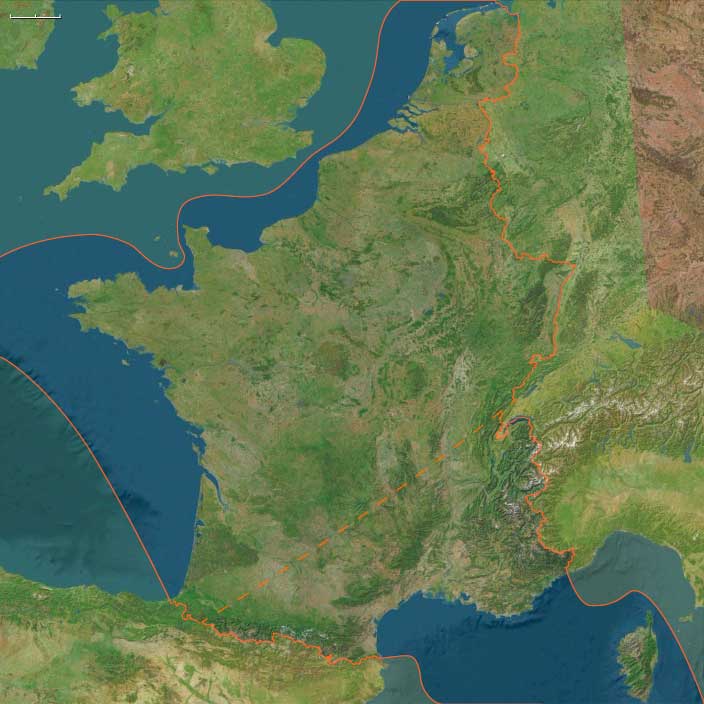
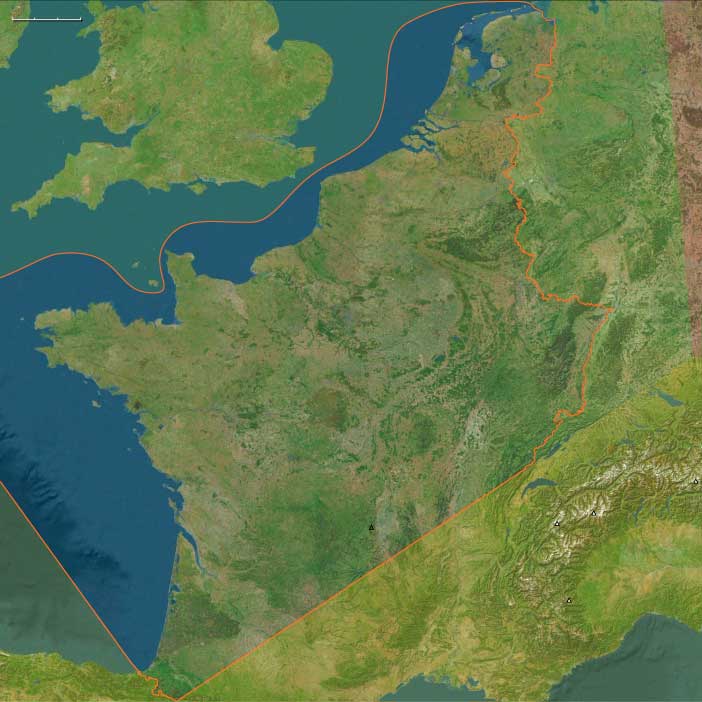
The Carolignian civil war (840–843) finally concludes in August 843, when Louis the German and Charles the Bald unite against Lothair I, forcing him to accept the Treaty of Verdun. This treaty formally divides the Carolingian Empire into three distinct kingdoms, setting the political and cultural foundations of medieval Europe.
Territorial Divisions Under the Treaty
- Charles the Bald (West Francia) → Receives all lands west of a line following the Scheldt, Meuse, and Saône rivers, the eastern mountains of the Massif Central, and the lower Rhône River. This kingdom forms the basis of modern France.
- Louis the German (East Francia) → Receives the lands of the Germanic peoples, forming the core of what will later become Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.
- Lothair I (Middle Francia) → Retains the imperial title and receives the Middle Kingdom, a narrow and unstable realm stretching from the North Sea to Italy, including Lotharingia, Burgundy, and northern Italy.
The Rise of Feudal Lords and the Decline of Royal Power
- With the breakup of the empire, feudal lords and church leaders gain greater autonomy, as central authority weakens.
- Local rulers consolidate power, undermining royal control and paving the way for fragmentation and decentralization in all three kingdoms.
- The rise of powerful feudal lords leads to greater regionalism, weakening the ability of Carolingian rulers to enforce uniform policies.
The Impact on Jewish Communities
- The political fragmentation brought on by feudalism adversely affects the position of Jews in all three kingdoms.
- As local rulers and church officials gain power, Jewish communities face increasing restrictions, particularly in trade and public life.
- Whereas some Carolingian rulers had protected Jewish merchants for their economic contributions, feudal lords and bishops, influenced by growing religious intolerance, often impose harsh policies and limit Jewish economic activities.
Legacy of the Treaty of Verdun
- Marks the true beginning of medieval France and Germany, as the linguistic and cultural divide between West and East Francia solidifies.
- The Middle Kingdom proves politically unstable, leading to further divisions and setting the stage for centuries of territorial disputes between France and Germany.
- The decline of Carolingian imperial unity accelerates the rise of feudal states, shaping the power structures of medieval Europe.
The Treaty of Verdun (843) not only ends the Carolingian civil war but also reconfigures the political landscape of Europe, with far-reaching consequences for governance, society, and minority communities in the medieval period.
Locations
People
Groups
- Jews
- Christianity, Chalcedonian
- Frankish, or Carolingian (Roman) Empire
- Francia Occidentalis (West Francia, or France), Kingdom of
- Francia Orientalis (East Francia), Kingdom of
- Francia Media (Middle Francia), Kingdom of