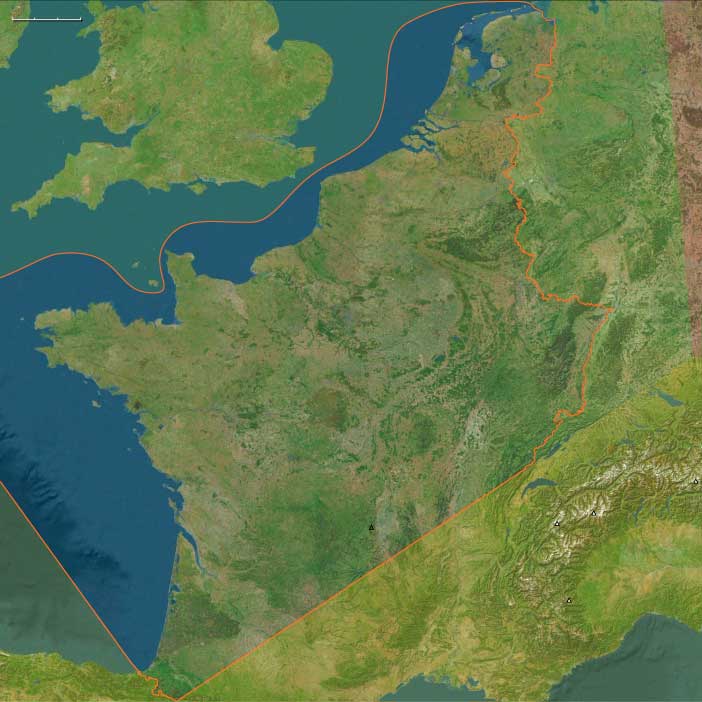
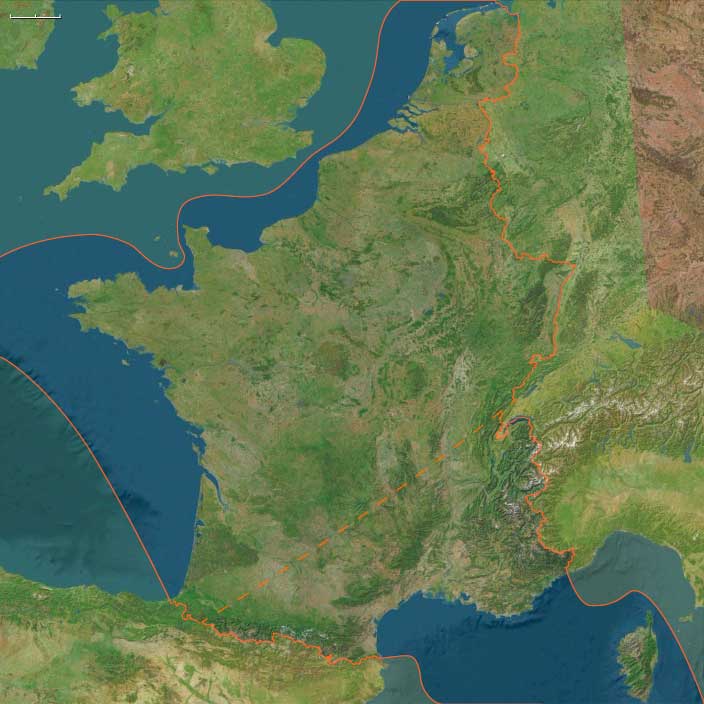
Atlantic West Europe
Related Events
Filter results
Showing 10 events out of 5003 total
The Atlantic World, a pentagonal region encompassing one twelfth of the Earth, includes the Azores, Madeira, northwestern Europe (including western Denmark and western Norway), the British Isles, the Orkney Islands, the Shetland Islands, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, Newfoundland, eastern and central North America, the northern section of Hispaniola, and several smaller island groups, notably Bermuda, the Bahamas, and the Turks and Caicos.
The eastern boundary, marked at 10° east longitude, divides Scandinavia into Eastern and Western sections, with Western Scandinavia oriented toward the North Atlantic and Eastern Scandinavia centered on the Baltic Sea Basin. This boundary also aligns with the historical eastern border of West Germany (1949–1990), before terminating in south-central Germany at its junction with the neighboring region to the southeast.
The western boundary, at 110° west longitude, cuts through Canada, separating the northern districts of Nunavut and the Northwest Territories from Alberta and Saskatchewan, approximately 75 miles south of the Alberta-Saskatchewan-Montana junction (48.1896851°N)—the northernmost point of the neighboring world to the southwest.
The southwestern boundary follows the division between the upper and lower Mississippi River Basin, then extends eastward into the Atlantic Ocean just south of Jacksonville, Florida, before terminating in northwestern Hispaniola.
HistoryAtlas contains 18,139 entries for The Atlantic World from the Paleolithic period to 1899.Narrow results by searching for a word or phrase or select from one or more of a dozen filters.
Prehistory of the Netherlands: A Landscape Shaped by Water
The prehistory of the region that is now the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and rivers, which continuously shifted the low-lying geography over millennia. The dynamic interplay of water and land influenced human settlement patterns, with early inhabitants gravitating toward higher ground as the landscape evolved.
Early Human Presence: Neanderthal Traces near Maastricht
- The oldest known human traces in the region belong to Neanderthals, whose presence dates back approximately 250,000 years.
- These remains have been discovered in higher, more stable soils near Maastricht, an area less affected by the flood-prone terrain of the lowlands.
- The Neanderthals likely adapted to a changing environment, utilizing the resources of rivers and forests for survival.
A Landscape in Constant Flux
Throughout prehistory, the region’s geological and climatic changes played a crucial role in shaping early habitation:
- Glacial and interglacial periods altered sea levels, periodically expanding and contracting habitable land.
- The Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt rivers created fertile but unstable floodplains, influencing settlement choices.
- Rising sea levels and sediment deposits led to the formation of peat bogs and coastal dunes, features that would later define the Dutch landscape.
These early environmental factors set the stage for the later development of prehistoric cultures, as humans adapted to a land in flux, balancing the challenges of water management with the rich resources provided by the rivers and coastlines.
The Moderns are taller, more slender, and less muscular than the Neanderthals, with whom they share—perhaps uneasily—the Earth.
Though their brains are smaller in overall size, they are heavier in the forebrain, a difference that may allow for more abstract thought and the development of complex speech.
Yet, the inner world of the Neanderthals remains a mystery—no one knows the depths of their thoughts or how they truly expressed them.
The fearsome cave bear (Ursus spelaeus) likely became extinct around 27,800 years ago, according to recent fossil reassessments.
Rather than a single cause, a combination of factors is believed to have led to its extinction. While overhunting by humans has largely been dismissed—since human populations at the time were too small to pose a significant threat—evidence suggests that cave bears and humans may have competed for shelter, particularly in caves.
Mitochondrial DNA research indicates that the cave bear's genetic decline began long before its extinction, ruling out climate change-induced habitat loss as the direct cause. However, a recent DNA study suggests that cave bear populations started declining around 50,000 years ago, coinciding with an increase in human populations.
Unlike its close relative, the brown bear, the cave bear was highly dependent on a vegetarian diet, making it less adaptable to environmental changes. Additionally, evidence suggests that cave bears exclusively used caves for hibernation, unlike brown bears, which could hibernate in thickets or other natural shelters. This specialized hibernation behavior likely contributed to high winter mortality when suitable caves were unavailable.
As human populations gradually expanded, both Neanderthals and anatomically modern humans increasingly occupied caves as living quarters, reducing the availability of essential hibernation sites for cave bears. Over time, this competition for shelter may have contributed to their gradual extinction.
Interestingly, cave bears are rarely depicted in prehistoric cave paintings, leading some researchers to speculate that human hunters may have avoided them, or that their habitat preferences simply did not overlap with early human settlements.
The invention of writing was not a single event, but rather a gradual evolution, preceded by the use of symbols, possibly originating for ritual or cultic purposes.
Researchers from the University of Victoria in Canada suggest that Neolithic cave painters employed symbolism as a form of early communication.
"...Von Petzinger and Nowell were surprised by the clear patterning of the symbols across space and time—some of which remained in use for over twenty thousand years.
Their research identifies twenty-six distinct signs, which may represent the earliest evidence of a graphic code used by humans shortly after their arrival in Europe from Africa—or possibly even earlier, suggesting they brought this practice with them.
If confirmed, these findings would support the growing body of evidence that the so-called "creative explosion"—once thought to have occurred later—actually began tens of thousands of years earlier than previously believed.
The rapid expansion of anatomically modern humans out of Africa, beginning around 60,000 years ago, appears to coincide with the development of new stone tool-making techniques.
These innovations, which define the Upper Paleolithic period, distinguish the stone tool culture of Homo sapiens sapiens from the previously similar technologies of Neanderthals and other archaic human groups.
Key advancements include:
- The production of long, narrow flake tools, known as blades, which could be fashioned into a variety of specialized tools,
- The emergence of bone and ivory artifacts, and
- The eventual development of clothing, often sewn together and adorned with beads.
These technological advancements likely played a crucial role in the success and adaptability of early modern humans as they spread across new environments.
Cultural practices associated with modern humans—such as the careful burial of the dead, the creation of elaborate cave art, and the decoration of everyday objects—emerge during this period, reflecting an increasing sense of ritual, symbolism, and aesthetic expression.
Neanderthal Burial and Bear Remains at Le Regourdou, France
At Le Regourdou, a prehistoric site in the Dordogne region of southern France, archaeologists will uncover a massive stone slab covering the remains of at least twenty bears, arranged in a rectangular pit. Nearby, the remains of a Neanderthal will be found in a separate stone-lined pit, accompanied by a collection of objects that suggest a deliberate burial.
Possible Ritual Significance
- The Neanderthal burial included items such as a bear humerus, a scraper, a core, and some flakes, which have been interpreted as grave offerings.
- The close proximity of Neanderthal remains and bear remains has led to speculation about a symbolic or ritual connection between Neanderthals and bears, possibly indicating:
- A ritualistic association with bears, perhaps related to beliefs about the afterlife.
- A functional use of bear remains in burial practices.
- A coincidence of site usage, where Neanderthals and bears occupied the same shelter at different times.
A Rare Glimpse into Neanderthal Culture
The Le Regourdou site provides compelling evidence of Neanderthal burial customs and potentially ritual behavior. Whether the bear remains were intentionally placed or coincidental, the site's structured layout and the presence of grave goods suggest that Neanderthals practiced deliberate burial and had symbolic or spiritual concepts.
This discovery reinforces the view that Neanderthals were not merely survival-driven hominins but had complex cultural and cognitive abilities, challenging earlier assumptions about their intellectual and social sophistication.
Around 55,000 years ago, global weather patterns begin to fluctuate dramatically, shifting from extreme cold to milder conditions and back within just a few decades.
By 50,000 years ago, the Wisconsin glaciation (known in Europe as the Würm glaciation) is well advanced. Expanding ice sheets in North America and Europe push climatic zones southward, transforming the temperate regions of Europe and North America into Arctic tundra-like landscapes. Meanwhile, rain bands typical of temperate zones shift south, reaching as far as northern Africa.
Neanderthals and Climate Adaptation
The Neanderthals, well adapted to cold climates with their barrel chests and stocky limbs, are better suited than Cro-Magnons to retain body heat. However, the rapid and unpredictable climate fluctuations cause ecological upheavals, replacing familiar plants and animals within a single lifetime—a shift to which Neanderthals struggle to adapt.
One major challenge is the replacement of forests by grasslands during the Mousterian Pluvial, an effect of the last Ice Age’s climatic shifts. This change disrupts the Neanderthals’ ambush-based hunting techniques, making it harder for them to secure food. As a result, large numbers of Neanderthals likely perish due to food scarcity and environmental stress, with the crisis peaking around 30,000 years ago.
Neanderthal Burial and Final Strongholds
Despite their decline, Neanderthals appear to be the first humans to intentionally bury their dead, often in simple graves. The last known traces of Mousterian culture, though lacking human remains, have been discovered at Gorham’s Cave on Gibraltar’s remote south-facing coast, dating between 30,000 and 24,500 years ago.
Possible Scenarios for Neanderthal Extinction
Several hypotheses attempt to explain the disappearance of the Neanderthals from the fossil record around 25,000 years ago:
-
Complete Extinction and Replacement: Neanderthals were a separate species from modern humans and became extinct due to climate change and/or competition with Homo sapiens, who expanded into their territories starting around 80,000 years ago. Anthropologist Jared Diamond suggests that violent conflict and displacement played a role in their demise.
-
Interbreeding and Absorption: Neanderthals were a contemporary subspecies that interbred with modern humans, gradually disappearing through genetic absorption.
-
Volcanic Catastrophe: A Campanian Ignimbrite super-eruption around 40,000 years ago, followed by a second eruption a few thousand years later, may have severely impacted Neanderthal populations. Evidence from Mezmaiskaya Cave in the Caucasus Mountains of southern Russia supports this theory, with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) analysis showing a distinct Neanderthal lineage separate from modern humans.
Energy Needs and Survival Challenges
Neanderthals had higher caloric requirements than any other known human species. They required 100 to 350 more calories per day than an anatomically modern human male (68.5 kg) or female (59.2 kg). This higher energy demand may have made them especially vulnerable when food sources became scarce, further contributing to their extinction.
Ultimately, by 25,000 years ago, Neanderthals disappear from the fossil record, leaving behind traces of their culture—but no direct descendants in the modern human genetic lineage.
As humans develop more advanced skills and techniques, evidence of early construction begins to emerge.
Fossil remains of Cro-Magnons, Neanderthals, and other Homo sapiens subspecies have been found alongside foundation stones and stone pavements arranged in the shape of houses, suggesting a shift toward settled lifestyles and increasing social stratification.
In addition to building on land, early humans also develop seafaring technology. The proto-Australians appear to be the first known people to cross open water to an unseen shore, ultimately peopling Australia—a remarkable achievement in early maritime exploration.