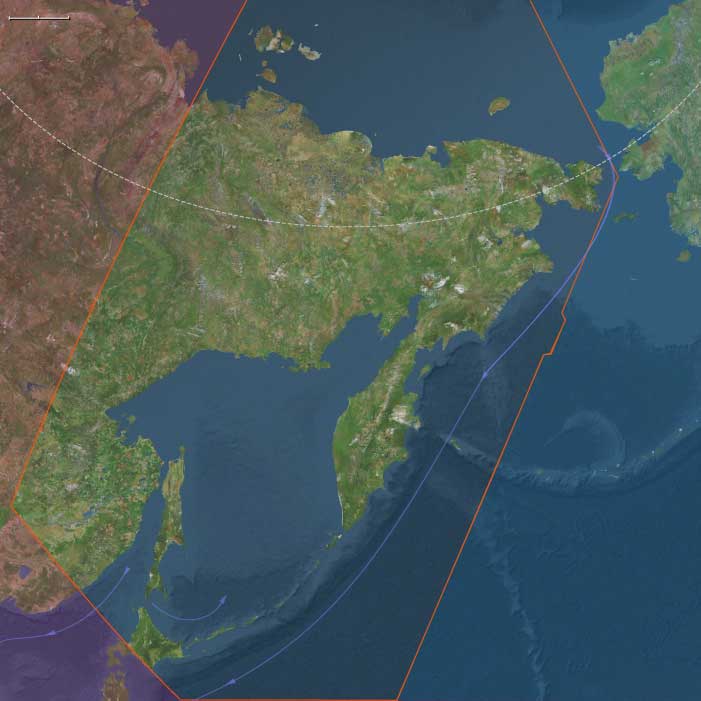
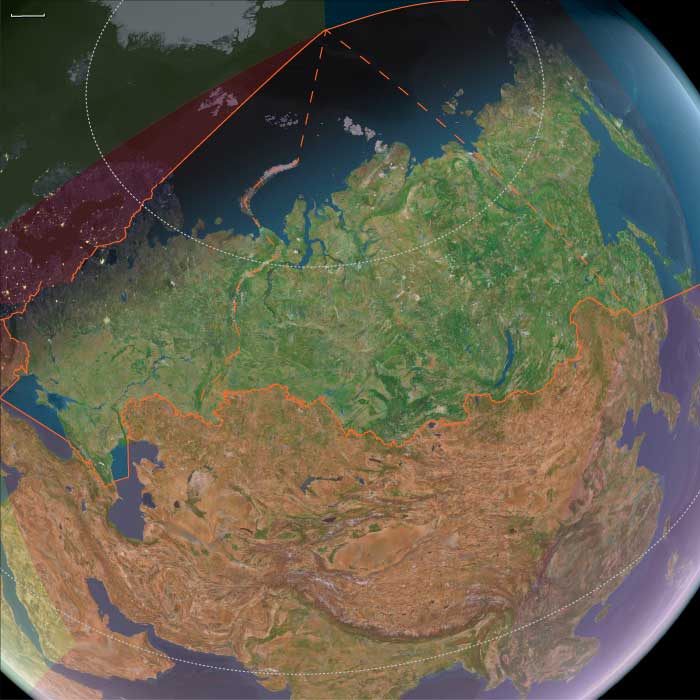
Northeast Asia
Related Events
Filter results
Showing 10 events out of 121 total
Northern Oceania encompasses Northeast Asia, North Polynesia, and Northwestern North America.
Its southeastern boundary extends from 48.1896851°N, approximately 75 miles south of the Alberta-Saskatchewan-Montana junction, to the Pacific Ocean at Cape Mendocino. To the immediate northwest of this line lies the Pacific Northwest.
In Canada, Alberta and British Columbia form the border with the United States, while to the north lie Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon, and Alaska.
The eastern boundary at 110°W was originally designated as the Fourth Meridian of the Dominion Land Survey. However, due to the limitations of early surveying techniques, the meridian was placed slightly west of this longitude. Since 1905, the Fourth Meridian has served as the entire boundary between Alberta and Saskatchewan and continues northward as the dividing line between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories above 70°N.
Northern Oceania's western boundary, at 130°E, roughly aligns with the division between Siberia and the Russian Far East, corresponding to Russia’s Siberian and Far Eastern federal districts. This boundary terminates above the Amur River, which has historically marked the border between Russia and China’s Heilongjiang province. The northernmost point of China, in Mohe City, lies along this river.
The southwestern boundary separates most of Japan’s northernmost major island, Hokkaido, from Honshu and the rest of the Japanese archipelago.
HistoryAtlas contains 401 entries for Northern Oceania from the Paleolithic period to 1899.
Narrow results by searching for a word or phrase or select from one or more of a dozen filters.
Northeastern Eurasia (49,293 – 28,578 BCE): Upper Pleistocene I — Steppe, Ice, and the Making of the Northern Corridor
Geographic and Environmental Context
During the late Pleistocene, Northeastern Eurasia extended from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific, encompassing the mammoth-steppe plains of East Europe and Western Siberia, the Altai–Yenisei uplands, and the Amur–Okhotsk–Bering frontier of Northeast Asia.
It was not a single region but a triadic system of worlds:
-
East Europe, the western steppe edge, framed by the Don, Dnieper, and Oka valleys — a land of loess terraces and braided rivers supporting dense megafaunal herds.
-
Northwest Asia, the Siberian interior, from the Urals through the Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei corridor to the Altai, where glacial basins and intermontane valleys served as refugia amid vast permafrost plains.
-
Northeast Asia, the Pacific rim and Beringian shelf, where tundra-steppe met coastal polynyas, bridging the continents long before human migration reached the New World.
Across these subregions, the environment graded from continental aridity in the west to maritime cold along the Pacific — a spectrum of adaptation that tied Eurasia together along its northern rim.
Climate and Environmental Shifts
The interval encompassed alternating Dansgaard–Oeschger warmings and Heinrich cold pulses leading into the Last Glacial Maximum.
-
In East Europe, permafrost advanced to the Dnieper and Don basins; vegetation alternated between steppe grassland and dwarf-shrub tundra.
-
In Northwest Asia, continental cold and aridity dominated; the Ob and Yenisei braided into unstable channels; loess and dust storms swept the forelands of the Urals and Altai.
-
In Northeast Asia, cold was tempered by oceanic moisture. Ice-edge upwellings in the Okhotsk and Bering seas sustained rich marine ecosystems, even as inland basins froze.
Periodic interstadial thaws re-greened the valleys, drawing herds northward and humans with them; stadials drove retreat to riverine refugia.
The result was a dynamic equilibrium of expansion and contraction rather than a single glacial standstill.
Lifeways and Settlement Patterns
All three worlds supported high-latitude foraging economies built on mobility, storage, and memory of place.
-
In East Europe, loess-terrace camps overlooked reindeer and mammoth migration corridors. Semi-recurrent bases at Kostenki, Sungir, and along the Dnieper combined hunting, butchery, and craft production.
-
In Northwest Asia, the Altai foothills and Minusinsk Basin hosted recurrent winter shelters, while open Ob–Yenisei valleys served for summer mammoth and bison hunts.
-
In Northeast Asia, river-mouth camps and coastal flats supported dual economies of inland big-game and maritime sealing and fishing. Seasonal movements linked river confluences, upland passes, and shelf-edge hunting grounds.
Each subregion achieved local stability through broad prey portfolios and cyclical mobility tuned to glacial rhythms.
Technology and Material Culture
A shared Upper Paleolithic technological grammar spanned the entire northern corridor:
-
Blade and microblade industries, adapted to portable composite weapons, formed the technological backbone from the Don to the Anadyr.
-
Bone, antler, and ivory were fashioned into points, awls, harpoons, and eyed needles — evidence for tailored fur clothing and cold-weather dwellings.
-
Obsidian sources in the Altai and Kamchatka and flint quarries in the Don basin anchored far-flung exchange networks.
-
Personal adornment — beads of tooth, ivory, shell, and amber — and ochre burials underscored enduring symbolic systems linking the Eurasian north to the rest of the Upper Paleolithic world.
The breadth of these parallels reveals not isolation but interoperability across extreme distance.
Movement and Interaction Corridors
Northeastern Eurasia was defined by movement — the continual negotiation between ice, water, and wind.
-
The Steppe–River Network: Don–Volga–Ural–Ob–Yenisei channels allowed seasonal following of herds and diffusion of tool types and ornaments.
-
The Altai–Mongolia Crossroads: A mountainous hinge connecting western and eastern populations, where genetic and cultural exchanges mixed Siberian and East Asian lineages.
-
The Amur–Okhotsk–Bering Rim: Shelf and river corridors provided both overland and coastal pathways toward Beringia, the eventual gateway to the Americas.
These arteries made the northern fringe not an end of settlement but a conveyor of innovation and populationbetween continents.
Cultural and Symbolic Expressions
Symbolic behavior mirrored subsistence breadth.
Engraved bones, ivory figurines, and ochred burials appear in all three subregions, expressing a shared spiritual engagement with animals and ancestors.
Altai and Don sites yield portable art and ivory figures, while the Amur and Lena valleys preserve carved bone and antler motifs of reindeer and mammoth.
Fire-ringed hearths and ritual hearth renewals suggest continuity of place and group identity across generations.
In these expressions, the northern peoples joined the global Upper Paleolithic symbolic sphere while imprinting it with an Arctic signature of endurance and cyclical return.
Environmental Adaptation and Resilience
Resilience depended on technological insulation, ecological diversity, and social connectivity.
Fur clothing, hide shelters, and stored fuel allowed wintering at 60–70° N; seasonal migration between coast, river, and plateau distributed risk; and wide alliance networks permitted exchange of mates, materials, and knowledge across immense ranges.
When one valley froze, another thawed — and people already knew the way.
Genetic and Linguistic Legacy
Populations rooted in this corridor carried the genetic foundations of later Arctic and Beringian peoples.
From East Europe through the Altai to the Amur, gene flow linked Eurasia’s west and east, seeding the ancestry of the First Americans and shaping linguistic substrates later echoed in circumpolar families.
Northeastern Eurasia thus became the cradle of the circumpolar continuum — a trans-Beringian cultural ecology that would persist for tens of millennia.
Transition Toward the Last Glacial Maximum
By 28,578 BCE, ice sheets and permafrost deepened, narrowing the habitable band to river valleys and steppe oases.
Yet humans remained throughout, their territories contracting but not vanishing.
The East European plains anchored the west, the Altai–Yenisei belt sustained the interior, and the Amur–Bering coast reached outward toward a new continent.
Northeastern Eurasia therefore stands as a model of The Twelve Worlds principle: its subregions were self-contained in ecology yet outward-looking in connection, bound less by shared geography than by the long, unbroken thread of movement — the first great northern highway of the human story.
Northeast Asia (49,293 – 28,578 BCE): Upper Paleolithic I — Mammoth-Steppe, Sheltered Coasts, and First Long Ranges
Geographic and Environmental Context
Northeast Asia includes eastern Siberia east of the Lena River to the Pacific, the Russian Far East (excluding the southern Primorsky/Vladivostok corner), northern Hokkaidō (above its southwestern peninsula), and extreme northeastern Heilongjiang.
-
Anchors: the Lower/Middle Amur and Ussuri basins, the Sea of Okhotsk littoral (Sakhalin, Kurils), Kamchatka, the Chukchi Peninsula (with Wrangel Island offshore), northern Hokkaidō, and seasonally emergent shelves along the Bering Sea and northwest Pacific.
Ancient North Siberians and the Deep Eurasian Split
The earliest securely identified human population associated with Northeast Asia belongs to a previously unknown lineage now termed the Ancient North Siberians (ANS). Genomic evidence from the Yana River sites (Yana RHS) indicates that these peoples were established in northeastern Siberia by at least 38,000 years ago, well before the Last Glacial Maximum.
The ANS diverged from Western Eurasians shortly after Western Eurasians themselves separated from East Asians, placing the ANS at a pivotal early junction in Eurasian population history. Culturally and biologically distinct, they adapted to extreme high-latitude environments long before the formation of later Siberian populations.
Crucially, these early inhabitants are not ancestral to most later Siberians and do not represent a continuous population into the Holocene. Instead, they form an early, now largely vanished branch of Eurasian humanity whose genetic legacy survives only in diluted form.
Climate and Environmental Shifts
-
Last Glacial Maximum (c. 26,500–19,000 BCE) dominated the latter half of this interval: colder, drier conditions; permafrost pushed south; sea level ~100 m lower exposed broad coastal plains.
-
Inland mammoth-steppe mosaics (grass–forb) alternated with open larch; coastlines were wider, with ice-edge polynyas supporting marine life.
Subsistence and Settlement
-
Big-game foraging focused on mammoth, woolly rhinoceros, horse, bison, and reindeer on river terraces (Aldan–Amur–Anadyr).
-
Coastal scouts used intertidal flats and pack-ice edges to take seals, walrus, seabirds, and winter fish.
-
Camps clustered at confluences, aeolian bluffs, and paleo-shorelines; repeated seasonal use left dense knapping scatters and hearths.
Technology and Material Culture
-
Blade and microblade industries from local obsidian (e.g., Hokkaidō, Kamchatka) and high-quality chert; hafted composite points for thrusting/spear-throwing.
-
Bone/antler/ivory harpoons, awls, eyed needles; tailored cold-weather clothing and boots.
-
Personal adornment: drilled tooth/shell pendants, beads, engraved bone; ochre widely used.
Movement and Interaction Corridors
-
River highways: Lena–Aldan–Amur trunks guided seasonal migrations.
-
Shelf-edge “kelp highway” along the Okhotsk–Bering coasts supported over-ice travel in winter and nearshore voyaging in summer.
-
Wrangel–Chukchi–Beringia arcs linked Northeast Asia to the sub-glacial refugium on the far side of the strait.
Cultural and Symbolic Expressions
-
Carved animal figurines and engraved bones reflect close predator–prey cosmologies.
-
Ochre burials and hearth-centered activity zones suggest shared Upper Paleolithic mortuary and domestic traditions.
Environmental Adaptation and Resilience
-
High mobility between coast–river–upland zones diversified diets and buffered risk.
-
Cold-weather tailoring, layered shelters (snow/skin windbreaks), and fuel provisioning enabled wintering at high latitudes.
Genetic and Linguistic Legacy
-
Ice-age Northeast Asian groups contributed key ancestry to Beringian populations; these, in turn, fed the founding gene pool of the First Americans.
-
Deep links formed here between Arctic–sub-Arctic foragers that later radiated across the North Pacific rim.
Transition Toward the Next Epoch
By 28,578 BCE, foragers in Northeast Asia had mastered periglacial ecologies and coastal shelves. As climate wobble and deglaciation approached, river and shoreline corridors would become even more crucial for movement, exchange, and eventual trans-Beringian dispersals.
Siberia has paleontological significance, as it contains bodies of prehistoric animals from the Pleistocene Epoch, preserved in ice or in permafrost.
Specimens of Goldfuss cave lion cubs, Yuka the mammoth and another woolly mammoth from Oymyakon, a woolly rhinoceros from the Kolyma, and bison and horses from Yukagir have been found.
One of the largest-known volcanic events of the last 251 million years of Earth's geological history formed the Siberian Traps.
Volcanic activity continued here for a million years and some scientists consider it a possible cause of the "Great Dying" about 250 million years ago, estimated to have killed 90% of species existing at the time.
Northeastern Eurasia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Late Pleistocene–Early Holocene — Beringian Migrations, Salmon Economies, and the First Pottery Traditions
Geographic & Environmental Context
At the end of the Ice Age, Northeastern Eurasia—stretching from the Urals to the Pacific Rim—was a vast, deglaciating world of river corridors, boreal forests, and emerging coasts. It included three key cultural–ecological spheres:
-
Northwest Asia — the Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei heartlands, Altai piedmont lakes, and Minusinsk Basin, bounded by the Ural Mountains to the west. Here, deglaciation produced pluvial lake systems, and forest belts climbed into the Altai foothills.
-
East Europe — from the Dnieper–Don steppe–forest margins to the Upper Volga–Oka and Pripet wetlands, a corridor of interlinked rivers and pluvial basins supporting rich postglacial foraging.
-
Northeast Asia — the Amur and Ussuri basins, the Sea of Okhotsk littoral, Sakhalin and the Kuril–Hokkaidō arc, Kamchatka, and the Chukchi Peninsula—a maritime–riverine realm where early Holocene foragers developed salmon economies and pottery traditions under the warming Pacific westerlies.
Together these subregions formed a continuous arc of adaptation spanning tundra, taiga, and coast—an evolutionary laboratory for the technologies and traditions that would later circle the entire North Pacific.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød (14,700–12,900 BCE): Rapid warming and higher precipitation expanded boreal forests and intensified riverine productivity across Eurasia’s north. Salmon runs strengthened in the Amur and Okhotsk drainages; pluvial lakes filled the Altai basins.
-
Younger Dryas (12,900–11,700 BCE): A temporary cold–dry reversal restored steppe and tundra, constraining forests to valleys; lake levels fell; inland mobility increased.
-
Early Holocene (after 11,700 BCE): Stable warmth and sustained moisture drove forest advance (pine, larch, birch) and high lake stands; sea levels rose along the Okhotsk and Bering coasts, flooding older plains and establishing modern shorelines.
These oscillations forged adaptable forager systems able to pivot between large-game mobility and aquatic specialization.
Subsistence & Settlement
Across the northern tier, lifeways diversified and semi-sedentism began to take root:
-
Northwest Asia:
Elk, reindeer, beaver, and fish formed broad-spectrum diets. Lakeside camps in the Altai and Minusinsk basins became seasonal home bases, while Ob–Yenisei channels hosted canoe or raft mobility. Forest nuts and berries expanded plant food options in warm phases. -
East Europe:
Along the Dnieper, Don, and Upper Volga, foragers targeted elk, red deer, horse, and beaver, exploiting riverine fish and waterfowl. Repeated occupations at lake outlets and confluences reflect increasing site permanence and food storage. -
Northeast Asia:
The Amur–Okhotsk region pioneered salmon-based economies, anchoring early Holocene villages at river confluences and estuarine terraces. Coasts provided seal, shellfish, seabirds, and seaweeds, while inland foragers pursued elk and musk deer. Winter sea-ice hunting alternated with summer canoe travel along the Sakhalin–Kuril–Hokkaidō chain.
This mosaic of economies—lake fishers, river hunters, and sealers—reflected the continent’s growing ecological diversity.
Technology & Material Culture
Innovation was continuous and regionally distinctive:
-
Microblade technology persisted across all subregions, with refined hafting systems for composite projectiles.
-
Bone and antler harpoons, toggling points, and gorges evolved for intensive fishing and sealing.
-
Ground-stone adzes and chisels appeared, enabling woodworking and boat construction.
-
Early pottery, first along the Lower Amur and Ussuri basins (c. 15,000–13,000 BCE), spread across the Russian Far East—among the world’s earliest ceramic traditions—used for boiling fish, storing oils, and processing nuts.
-
Slate knives and grindstones at Okhotsk and Amur sites show specialized craft economies.
-
Personal ornaments in amber, shell, and ivory continued, while sewing kits with eyed needles and sinew thread supported tailored, waterproof clothing.
These toolkits established the technological template for later northern and Pacific Rim foragers.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei river systems funneled movement north–south, linking the steppe with the taiga and tundra.
-
Altai and Ural passes maintained east–west contact with Central Asia and Europe.
-
Dnieper–Volga–Oka networks merged the European forest-steppe into the greater Eurasian exchange field.
-
In the Far East, the Amur–Sungari–Zeya–Okhotsk corridor unified interior and coast, while the Sakhalin–Kuril–Hokkaidō arc allowed short-hop voyaging.
-
Across the Bering Strait, fluctuating sea levels intermittently connected Chukotka and Alaska, maintaining Beringian gene flow and cultural exchange.
These conduits supported both biological and technological diffusion at a continental scale.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ochre burials with ornamented clothing and ivory or antler goods reflect deep symbolic continuity from the Upper Paleolithic.
-
Petroglyphs and engravings in the Altai and Minusinsk basins, and later in Kamchatka, depict large animals, waterbirds, and solar motifs.
-
Amur basin figurines and carved marine-mammal and fish effigies attest to ritualized relationships with food species.
-
In the Far East, early evidence of first-salmon and bear-rite traditions foreshadows later Ainu and Okhotsk ceremonialism.
Across all subregions, water and game remained the core of spirituality, connecting people to cyclical abundance and ancestral landscapes.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Foragers across Northeastern Eurasia met environmental volatility with creative versatility:
-
Zonal mobility (taiga–tundra–coast) and multi-season storage (dried meat, smoked fish, rendered oils) stabilized food supply.
-
Boat and ice technologies extended reach across seasons.
-
Broad-spectrum diets cushioned against climatic downturns.
-
Flexible dwellings and social alliances allowed fission and fusion as resources shifted.
-
Memory landscapes—engraved rocks, ritual mounds, named rivers—preserved continuity through spatial change.
Genetic and Linguistic Legacy
The Beringian population standstill during the Late Glacial created a deep ancestral pool for both Paleo-Inuit and First American lineages, while reciprocal migration reconnected Chukchi, Kamchatkan, and Amur populations after sea-level rise.
These long-lived networks seeded circum-Pacific cultural parallels in salmon ritual, dog-traction, maritime hunting, and composite toolkits, forming the northern backbone of later trans-Pacific cultural continuity.
Long-Term Significance
By 7,822 BCE, Northeastern Eurasia had become one of the world’s great centers of forager innovation:
-
Northwest Asia’s pluvial lakes fostered early semi-sedentism and the first rock art of Siberia.
-
East Europe’s river–lake foragers stabilized broad-spectrum economies bridging steppe and forest.
-
Northeast Asia’s salmon-rich coasts and early pottery traditions created the technological and ritual matrix that would radiate across the North Pacific.
This continental synthesis of aquatic resource mastery, ceramic innovation, and long-range mobility defined the emerging Holocene north—a zone where people and landscape adapted together through water, ice, and memory.
Northeast Asia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper Paleolithic II — Beringian Standstill, Early Pottery Horizons, and Salmon Towns
Geographic and Environmental Context
Northeast Asia includes eastern Siberia east of the Lena River to the Pacific, the Russian Far East (excluding the southern Primorsky/Vladivostok corner), northern Hokkaidō (above its southwestern peninsula), and extreme northeastern Heilongjiang.
-
Anchors: the Lower/Middle Amur and Ussuri basins, the Sea of Okhotsk littoral (Sakhalin, Kurils), Kamchatka, the Chukchi Peninsula (with Wrangel Island offshore), northern Hokkaidō, and seasonally emergent shelves along the Bering Sea and northwest Pacific.
Climatic Crisis and Population Transformation During the LGM
Between roughly 28,500 and 20,000 years ago, the onset of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) profoundly altered Northeast Asia. Ice sheets, permafrost expansion, and ecological fragmentation reduced habitable zones across Siberia.
During and immediately after this period, the Ancient North Siberians were largely replaced by populations carrying ancestry closely related to East Asians. This was not a simple migration but a prolonged process of demographic turnover, admixture, and regional extinction.
Out of this transformation emerged two closely related populations:
-
Ancestral Native Americans
-
Ancient Paleosiberians (AP)
Paleoclimatic modeling strongly supports southeastern Beringia as a long-term refugium during the LGM, providing a stable ecological zone where these populations could persist, interact, and differentiate.
Climate and Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød (c. 14,700–12,900 BCE): warming and moisture increase expanded boreal forest into valleys; salmon runs intensified; nearshore productivity rose.
-
Younger Dryas (c. 12,900–11,700 BCE): brief return to cooler, drier conditions; tundra patches expanded but ice-free coasts still offered reliable marine resources.
-
Early Holocene (after c. 11,700 BCE): stabilizing warmth and rising sea level reshaped shorelines; taiga expanded fully; rich riverine and estuarine habitats matured.
Subsistence and Settlement
-
Deglaciating coasts supported seal and salmon economies; intertidal shellfish beds and seabird rookeries fueled seasonal aggregation.
-
In warming phases, diets diversified toward fish (salmon, sturgeon), small game, and plant foods (nuts, roots, berries).
-
Younger Dryas prompted higher mobility and renewed emphasis on large herbivores where herds persisted.
-
Early Holocene villages favored river confluences and coastal terraces, ideal for salmon weirs and broad foraging radii.
Technology and Material Culture
-
Microblade production refined; hafted composite points standardized for hunting and sealing.
-
Bone/antler harpoons with toggling tips; barbed fishhooks; sewing kits for tailored garments and waterproof seams.
-
Early pottery appears in the Lower Amur–Russian Far East and spreads to surrounding basins—among the world’s earliest ceramic traditions—used for fish oils, stews, and nut processing.
-
Ground-stone adzes for wood-working and dugout canoe manufacture; slate knives on some Okhotsk coasts.
Movement and Interaction Corridors
-
Amur–Sungari waterway integrated interior and coast; Sakhalin–Kuril–Hokkaidō island chain enabled short-hop voyaging.
-
Beringian standstill: populations on both sides of the strait developed long-term ties; fluctuating sea levels modulated contact.
-
Seasonal sea-ice bridges facilitated winter travel; summer lanes favored canoe movement.
Cultural and Symbolic Expressions
-
Carved bone and ivory figurines, zoomorphic engravings, and ochre burials persisted, signaling continuity with earlier Upper Paleolithic symbolic systems.
-
Recurrent salmon first-catch rites and bear/sea-mammal treatment practices are inferred from patterned discard and ritualized processing locales.
Environmental Adaptation and Resilience
-
Zonal mobility (taiga–tundra–coast) and storage (dried fish, rendered oils) buffered climate swings across Bølling–Allerød → Younger Dryas → Early Holocene.
-
Canoe technologies, fish weirs, and shoreline mapping (capes, tide rips, haul-outs) underwrote stable subsistence as forests spread and shorelines shifted.
Genetic and Linguistic Legacy
-
Prolonged Beringian population structure during late glacial–early Holocene times contributed ancestry to Paleo-Inuit and to the First Americans; reciprocal gene flow linked Chukchi–Kamchatka–Amur families.
-
These deep ties foreshadowed later circum-North Pacific cultural continuities in salmon ritual, dog-traction, and composite toolkits.
Transition Toward the Holocene Forager Horizons
By 7,822 BCE, Northeast Asia featured mature taiga coasts, prolific salmon rivers, and early pottery villages—a landscape primed for the broad-spectrum, semi-sedentary foraging economies that would dominate the Early Holocene and eventually feed into Epi-Jōmon/Satsumon, Okhotsk, and Amur basin cultural florescences.
Mitochondrial haplogroups A, B, and G originated fifty thousand years ago, and the bearers subsequently colonized Siberia, Korea and Japan, by thirty five thousand years ago.
Parts of these populations migrate to North America.
The Transition into the Holocene: Climate Change, Human Migration, and Environmental Transformations
During this epoch, the Northern Hemisphere experienced significant warming, accelerating the deglaciation processand causing rising sea levels as ice sheets continued to melt. This climatic shift marked the transition into the Holocene epoch, a period of relative climate stability following the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM).
Glacial Retreat and Human Recolonization
- Land ice receded from Denmark and southern Sweden, opening up new habitable territories.
- Human populations, previously confined to refuge areas, began repopulating Eurasia as ice sheets withdrew.
- For the first time, humans crossed Beringia into North America, initiating the peopling of the Americas.
The Atlantis Narrative and Speculative Cataclysmic Events
According to Plato's dialogues Timaeus and Critias (circa 360 BCE), the legendary island of Atlantis—described as lying “in front of the Pillars of Hercules” (modern Straits of Gibraltar)—was said to have sunk around 10,000 years earlier along with its advanced civilization.
Some researchers speculate that a cataclysmic event of global significance may have occurred around 9577 BCE, potentially involving:
- Crustal shifts and a possible axial tilt of the Earth
- Mass extinctions of animal species
- The formation of new mountain ranges
- Significant alterations in landmasses
- Massive volcanic eruptions and earthquakes
While no definitive evidence supports a single catastrophic event, glacial retreat after the 11th millennium BCEreshaped landscapes and ecosystems worldwide.
Climate Shifts and Desertification
As the climate stabilized, new regional climate patterns emerged:
-
Permanent Mediterranean climates developed in regions such as:
- The Mediterranean Basin
- California
- Southwestern Australia
- Chile
- Southwestern Africa
-
Desertification gradually encroached upon subtropical regions, fundamentally transforming ecosystems and influencing early human settlements.
This period marked a turning point in human history, as warmer, stable climates allowed for agricultural developments, leading to the eventual rise of Neolithic societies and early civilizations.
The Conclusion of the Quaternary Extinction Event (c. 8th Millennium BCE)
The Quaternary extinction event, which began in the mid-Pleistocene, reached its final phase by the start of the 8th millennium BCE. By this time, many of the iconic Ice Age megafauna had disappeared, fundamentally reshaping ecosystems across the globe.
Major Megafaunal Losses
Among the most significant species lost during this period were:
- Megatherium – The giant ground sloths of the Americas, once towering over human hunters.
- Woolly rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis) – Adapted for Ice Age steppe-tundra, but unable to survive post-glacial warming.
- Irish elk (Megaloceros giganteus) – Famous for its massive antlers, which may have been a factor in its extinction.
- Cave bear (Ursus spelaeus) – A large Ice Age omnivore, extinct by 27,000 years BP, foreshadowing later megafaunal extinctions.
- Cave lion (Panthera spelaea) – One of the largest predatory cats of prehistoric Europe and Asia.
- Saber-toothed cats (Smilodon and Homotherium) – Iconic apex predators that disappeared with declining megafaunal prey.
The Extinction of the Mammoth and Equids
- Mammoths (Mammuthus primigenius) vanished from Eurasia and North America around this time.
- However, isolated populations on Wrangel Island (Arctic Ocean) survived until around 1650 BCE, among the last remnants of the Ice Age giants.
- Equidae (horses and related species) disappeared entirely from North America, where they had evolved.
- While horses, donkeys, and zebras persisted in Africa and Eurasia, wild horses in the Americas vanished, only to be reintroduced by humans in the 16th century CE.
Causes of the Final Extinctions
The final wave of Quaternary extinctions is attributed to two primary factors:
-
Climate Change
- The end of the Ice Age caused habitat shifts, reducing grazing lands for megafauna.
- Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns disrupted ecosystems that large herbivores depended on.
-
Human Expansion and Overhunting
- Advanced human hunting techniques (e.g., mass kills, fire-driven hunts, and spears with stone points) increased predation pressure.
- Human presence often correlated with the disappearance of large prey species, particularly in North and South America.
The Legacy of the Quaternary Extinction
- This massive loss of megafauna reshaped global ecosystems, leaving many regions without their largest herbivores and predators.
- It marked a critical turning point in Earth's biological history, influencing later human societies, as they shifted from big-game hunting toward domesticated animals and agriculture in the Holocene.
- Some species that disappeared in the wild, like the horse, would later be reintroduced and domesticated, altering human civilization forever.
The Quaternary extinction event was one of the most profound biological transitions in prehistory, signaling the end of the Pleistocene megafaunal era and the beginning of the human-dominated Holocene epoch.
Northeastern Eurasia (7,821 – 6,094 BCE): Early Holocene — Salmon Rivers, Pottery Frontiers, and Forest–Sea Corridors
Geographic & Environmental Context
From the Upper Volga–Oka and Dnieper–Pripet belts across the Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei to the Amur–Ussuri and the Okhotsk–Bering rim (Sakhalin, Kurils, Kamchatka, Chukchi, northern Hokkaidō), Northeastern Eurasia formed a continuous world of taiga, big rivers, and drowned estuaries. Sea level rise reshaped river mouths into productive bays and tidal flats; inland, lake chains and marshlands multiplied along stabilized watersheds.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
The Holocene thermal optimum brought warmer, wetter, and more even seasonality.
-
Taiga expansion (birch–pine–spruce) advanced north; mixed forests with hazel spread south.
-
Rivers (Volga, Dnieper, Ob, Yenisei, Amur) ran full but steady; estuaries and kelp-lined nearshore waters boomed.
-
Rising seas drowned river mouths, creating ideal passages for anadromous salmon and shellfish-rich flats.
These conditions favored semi-sedentary clustering at confluences, terraces, and tidal margins.
Subsistence & Settlement
A pan-regional broad-spectrum, storage-oriented foraging system matured:
-
East Europe (Upper Volga–Oka, Dnieper, Upper Dvina, Pripet): semi-sedentary river villages with pit-houses focused on sturgeon/pike, elk/boar, hazelnuts, and berries; net-weirs and fish fences anchored seasonal peaks.
-
Northwest Asia (Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei, Altai–Minusinsk): riverine hamlets hunted elk, reindeer, boar; salmon and sturgeon fisheries underwrote wintering; hearth clusters and storage pits marked long occupation.
-
Northeast Asia (Lower/Middle Amur–Ussuri, Okhotsk littoral, Sakhalin–Kurils–Hokkaidō, Kamchatka, Chukchi): salmon-focused semi-sedentism at confluences and tidal flats; smoke-drying and oil rendering produced high-calorie stores; broad-spectrum rounds added elk/reindeer, waterfowl, intertidal shellfish, and seasonal pinnipeds.
Across the span, households returned to the same terraces, bars, and headlands, building place-memory landscapes suited to storage and exchange.
Technology & Material Culture
This was the first great pottery horizon of the north, paired with refined fishing and woodcraft:
-
Early ceramics (7th millennium BCE onward): fiber-/plant- or grit-tempered jars spread in the Upper Volga–Oka, Ob–Yenisei, and Lower Amur, used for boiling fish/meat, fat rendering, and storage; soot-blackened cookpots are typical in the Amur basin.
-
Ground-stone adzes/axes drove canoe- and house-carpentry; composite harpoons, barbed bone hooks, gorges, net sinkers/floats, and stake-weirs scaled mass capture.
-
Personal ornaments of shell, amber, antler, and drilled teeth traveled widely; ochre accompanied burials.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
Waterways made a braided superhighway:
-
Volga–Oka–Dnieper–Dvina canoe circuits linked taiga, marsh, and lake belts; portages stitched watersheds and spread pottery styles.
-
Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei integrated western and central Siberia; the Ural corridor connected taiga foragers with the forest-steppe of Europe.
-
Amur–Sungari tied interior to coast; short-hop voyaging along Sakhalin–Kurils–Hokkaidō moved shell, stone, and ideas; over-ice travel on inner bays persisted in winter.
These lanes provided redundancy—if a salmon run failed locally, neighboring reaches or coastal banks supplied substitutes.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
A river-and-animal cosmology left vivid traces:
-
Rock art fields (Minusinsk, Tomsk, Karelia–Alta–Finland) depict elk, fish, boats, hunters, and ritual poses.
-
First-salmon rites are inferred in patterned discard and special hearths; bear and sea-mammal treatments suggest respect for “animal masters.”
-
Cemeteries with ochre, antler and stone grave goods, and—in the northeast—pots in burials formalized ancestry tied to landing places and weirs.
Waterfront mounds and shell/bone-rich zones functioned as ancestral monuments.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Resilience rested on storage + mobility + multi-habitat rounds:
-
Smoke-dried fish, rendered oils, roasted nuts/berries, and cached meats carried camps through winter.
-
River–coast–upland scheduling diversified risk across salmon runs, waterfowl peaks, reindeer/elk migrations, and shellfish seasons.
-
Weir and landing-place tenure, reinforced by ritual, regulated pressure on key stocks and limited conflict.
Long-Term Significance
By 6,094 BCE, Northeastern Eurasia had consolidated into a storage-rich taiga and salmon civilization without agriculture—large, long-lived villages on river terraces and tidal flats; early pottery embedded in daily subsistence; and canoe/ice corridors knitting thousands of kilometers.
These habits—fat economies, ceramic storage, engineered fisheries, and shrine-marked tenure—prepared the ground for larger pit-house villages, denser coastal networks, and, later, steppe–taiga exchanges that would link this northern world to Eurasia at large.