Northern Australia — 49,293–28,578 BCE Northern …
Years: 49293BCE - 28578BCE
Northern Australia — 49,293–28,578 BCE
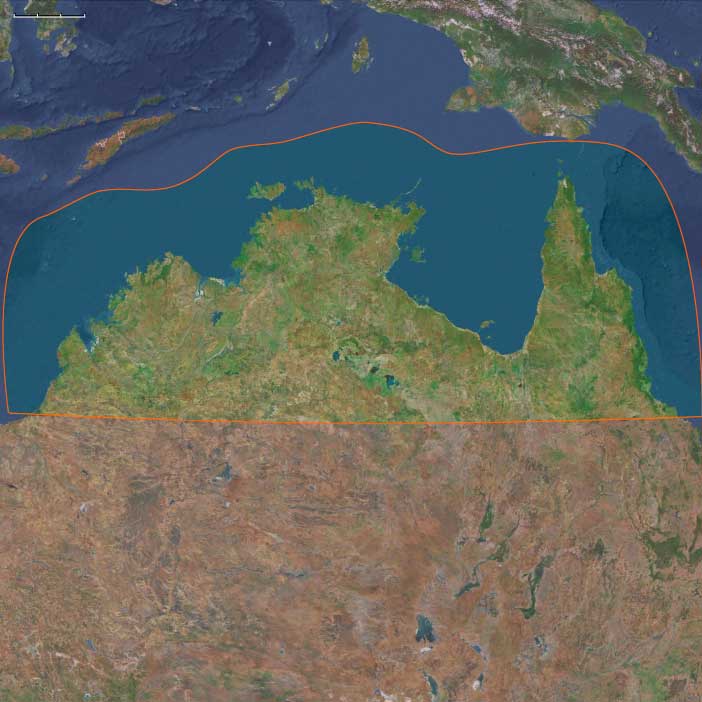
Northern Australia includes Top End and Arnhem Land, Kimberley, Cape York & Gulf of Carpentaria, Pilbara north, connected via the Sahul Shelf to southern New Guinea at lowstand.
Anchors: Arnhem Land escarpment, Kimberley plateau gorges, Gulf Plains, Cape York rainforests and Great Barrier Reef shelf, Carpentaria mega-embayment.
Geographic & Environmental Context
-
Sahul landmass joined Australia–New Guinea across the Arafura/Carpentaria shelves; Gulf of Carpentaria held a large inland sea/megapalustrine system late in the window.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
LGM: stronger seasonality; monsoon weakened/contracted; inland aridity; coastal upwelling maintained marine productivity.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Continuous human occupation: rock-shelter and open-air sites in Arnhem Land, Kimberley, Cape York.
-
Coastal: shellfish, fish, turtles, dugong; estuary and reef exploitation on expanded shelf flats.
-
Inland: macropods, emu, small game; plant foods (yams, cycads processed).
-
-
Megafauna declining toward the end of this epoch.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Flake/blade industries; early ground ochre; hafted points emerging; resin adhesives; wooden/fiber technologies pervasive.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Shelf-edge coasts and river corridors; Sahul routes into southern New Guinea; seasonal moves between coast and stone-country uplands.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Earliest rock art phases (engraving/paint); body painting; marked burial/cremation traditions in some regions.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Estate-based mobility tracking monsoon resources; shelf foraging buffered dry interiors.
Transition
-
Deglaciation will raise seas, fragmenting shelf landscapes into modern coasts/reefs and reshaping mobility.