Near East (909 BCE – 819 …
Years: 909BCE - 819
Near East (909 BCE – 819 CE) Early Iron and Antiquity — Greeks of Ionia, Levantine Tyre, Roman–Byzantine Egypt, Arabia’s Caravans
Geographic and Environmental Context
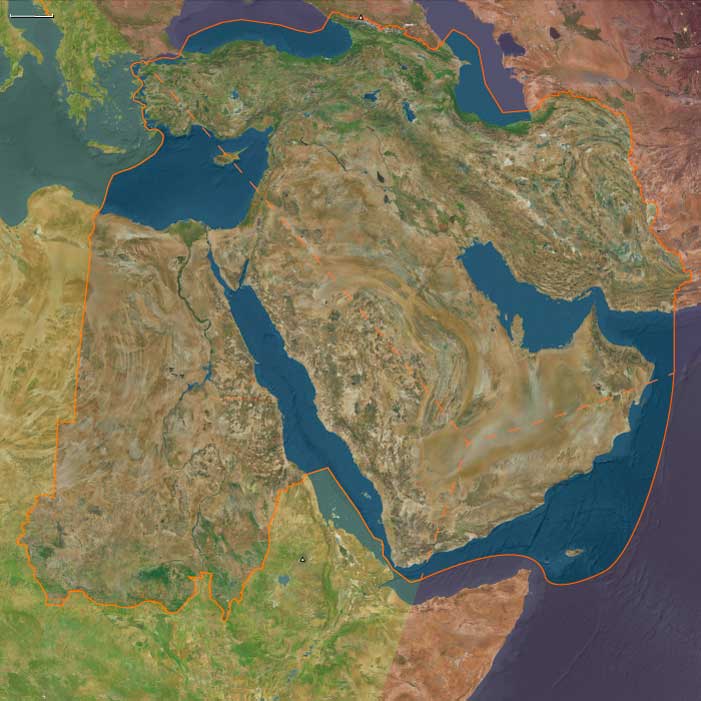
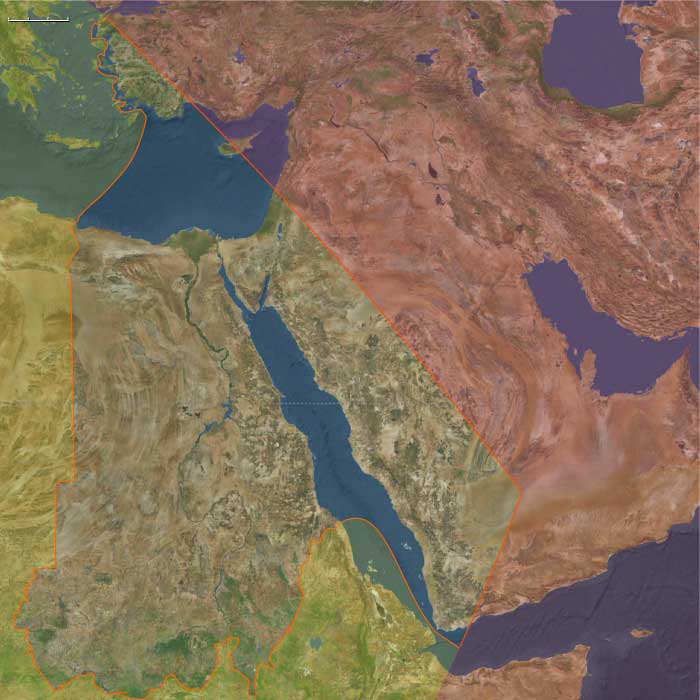
The Near East includes Egypt, Sudan, Israel, most of Jordan, western Saudi Arabia, western Yemen, southwestern Cyprus, and western Turkey (Aeolis, Ionia, Doris, Lydia, Caria, Lycia, Troas) plus Tyre (extreme SW Lebanon).-
Anchors: the Nile Valley and Delta; Sinai–Negev–Arabah; the southern Levant (with Tyre as the sole Levantine node in this subregion); Hejaz–Asir–Tihāma on the Red Sea; Yemen’s western uplands/coast; southwestern Cyprus; western Anatolian littoral (Smyrna–Ephesus–Miletus–Halicarnassus–Xanthos; Troad).
Climate & Environment
-
Nile’s late antique variability; Aegean storms seasonal; Arabian aridity persistent but terraces/cisterns mitigated.
Societies & Political Developments
-
Western Anatolia Greek city-states (Ionia–Aeolia–Doria, with Troad): Miletus, Ephesus, Smyrna, etc.
-
Tyre (sole Near-Eastern Levantine node here) dominated Phoenician seafaring.
-
Egypt (Ptolemaic → Roman → Byzantine): Nile granary and Christianizing hub.
-
Arabian west: caravan kingdoms and Hejaz–Asir oases; western Yemen incense terraces and caravan polities.
-
Southwestern Cyprus embedded in Hellenistic–Roman maritime circuits.
Economy & Trade
-
Grain–papyrus–linen from the Nile; olive–wine Aegean; incense–myrrh from Yemen; Red Sea lanes linked to Aden–Berenike nodes (outside core but connected).
-
Tyre exported craft goods and purple dye.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Iron agriculture and tools; triremes and merchant galleys; advanced terracing, cisterns; lighthouse/harbor works.
Belief & Symbolism
-
Egyptian polytheism → Christianity (Alexandria); Greek civic cults; Tyrian traditions; Arabian deities; monasticism along Nile/Desert.
Adaptation & Resilience
-
Canal maintenance buffered Nile shocks; terraces/cisterns stabilized Arabian farming; Aegean coastal redundancy protected shipping routes.
Transition
By 819 CE, the Near East was a multi-corridor world of Nile granaries, Ionia’s city-coasts, Tyre’s Phoenician legacy, and Arabian incense roads — a foundation for the medieval dynamics ahead (Ayyubids in Syria/Egypt next door, Abbasids beyond, and the Ionian–Anatolian littoral under Byzantine/Nicaean arcs).
People
Groups
- Egyptians
- Polytheism (“paganism”)
- Nubians
- Tyre, Kingdom of (Phoenicia)
- Minaean Kingdom
- Philistines
- Arab people
- Babylon, Kingdom of
- Egypt (Ancient), Third Intermediate Period of
- Kush, Kingdom of
- Judah, Kingdom of
- Israel (Northern Kingdom of)
- Assyria, (New) Kingdom of (Neo-Assyrian Empire)
- Sheba, or Saba, Kingdom of
- Assyria, (New) Kingdom of (Neo-Assyrian Empire)
- Egypt (Ancient), Late Period of
- Qataban
- Judahites
- Babylonia, Classical
- Achaemenid, or First Persian, Empire
- Jews
- Qataban, Kingdom of
- Alexander, Empire of
- Cyprus, Hellenistic
- Egypt, Alexandrine
- Greeks, Hellenistic
- Egypt, Ptolemaic Kingdom of
- Hasmonean dynasty
- Himyarite Kingdom
- Hasmonean dynasty
- Judea, Roman client kingdom of
- Egypt (Roman province)
- Judea (Roman province)
- Christians, Jewish
- Persian Empire, Sassanid, or Sasanid
- Christianity, Nicene
- Christian community of Najran
- Egypt, Diocese of
- Christians, Eastern (Diophysite, or “Nestorian”) (Church of the East)
- Christians, Miaphysite (Oriental Orthodox)
- Christians, Monophysite
- Christianity, Chalcedonian
- Himyar
- Egypt, Eastern Roman (Byzantine)
- Rashidun Caliphate
- Filastin (Caliphal Palestine)
- Christians, Monotheletist
- Egypt in the Middle Ages
- Muslims, Sunni
- Muslims, Kharijite
- Umayyad Caliphate (Damascus)
- Muslims, Shi'a
- Syrian people
- Muslims, Ibadi
- Umayyad Caliphate (Harran)
- Abbasid Caliphate (Kufa)
- Abbasid Caliphate (Baghdad)
Topics
- Iron Age, Near and Middle East
- Maccabees, Revolt of the
- Jewish–Roman wars
- First Jewish-Roman War, or Jewish Revolt of 66-73
- Kitos War, or Second Jewish-Roman War, or Jewish Revolt of 115-17
- Third Jewish-Roman War, or Bar Kokhba's Revolt
- Muslim Conquest of the Levant
- Muslim Conquest of Egypt
Commodoties
- Rocks, sand, and gravel
- Glass
- Domestic animals
- Oils, gums, resins, and waxes
- Grains and produce
- Textiles
- Fibers
- Strategic metals
- Lumber
- Money
- Aroma compounds
- Spices
Subjects
- Commerce
- Language
- Symbols
- Writing
- Architecture
- Engineering
- Faith
- Government
- Custom and Law
- Metallurgy