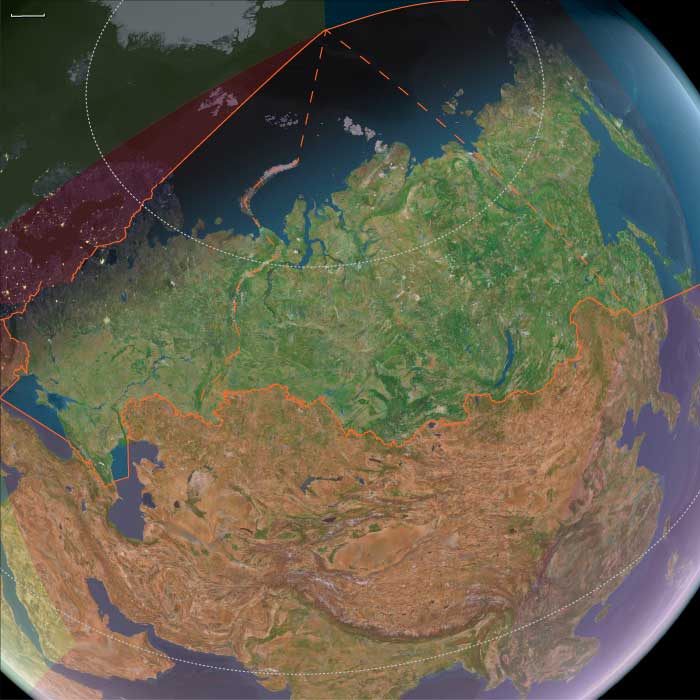
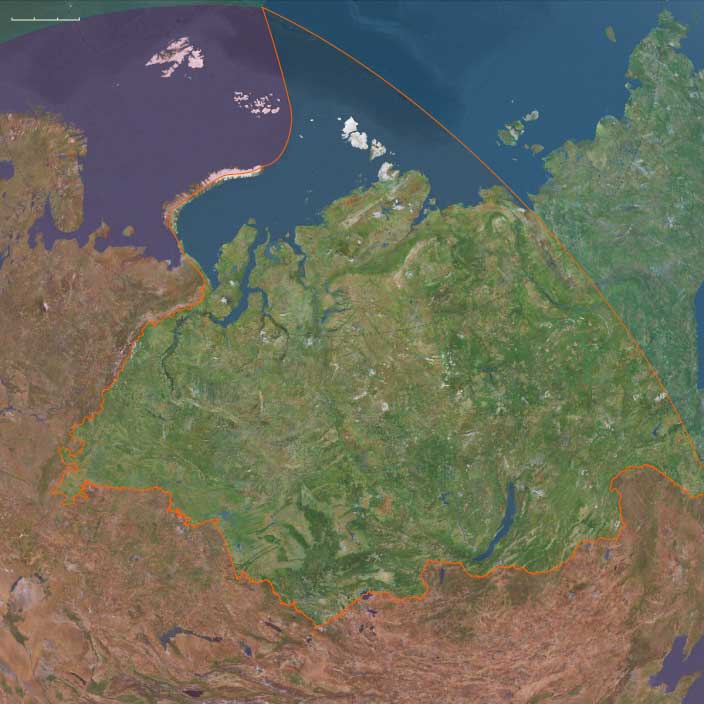
The Tunguska Event fells millions of trees …
Years: 1908 - 1908
June
Most scientists believe this was the result of an air burst of a meteor or a comet.
Even though no crater has ever been found, the landscape in the sparsely inhabited area still bears the scars of this event.
Locations
Groups
Subjects
Regions
Subregions
Related Events
Filter results
Showing 10 events out of 8195 total
American heavyweight boxer Jack Johnson defeats Tommy Burns in Australia in 1908 and becomes the first black to hold the world title.
The white-controlled boxing world immediately begins its quest for a “great white hope” to wrest the championship from the outspoken and flamboyant Johnson.
The University of the Philippines is founded at Manila in 1908.
His family, which includes eight children besides himself, is devoutly Jewish and, like the majority of the some twenty thousand Jews in Vitebsk, humble without being poverty-stricken; the father works in a herring warehouse, and the mother runs a shop where she sells fish, flour, sugar, and spices.
Young Marc attended the heder, the Jewish elementary school, and later on he went to the local public school, where instruction was in Russian.
After learning the elements of drawing at school, he studied painting in the studio of a local realist, Jehuda Pen, and in 1907 went to St. Petersburg, where he studies intermittently, eventually under Léon Bakst, who is beginning a brilliant career as a stage designer.
Characteristic works of this period of early maturity are the nightmarish The Dead Man (1908; Amsterdam Stedelijk Museum, Amsterdam, Musée National d'Art Moderne, Centre Georges Pompidou, Paris, France), in which a roof violinist is already present.
Austria-Hungary uses powers granted her under the Berlin Conference, to formally annex Bosnia-Hercegovina in 1908 with Russia assent.
Corinth has begun to devote much of his time to fighting the rise of Expressionism, a style that he has unwittingly helped to foster.
Kandinsky between 1903 and 1908 travels extensively, from Holland to as far south as Tunisia and from Paris back to Russia, stopping off for stays of several months each in Kairouan (Tunisia), Rapallo (Italy), Dresden, the Parisian suburb of Sèvres, and Berlin.
Kokoschka in 1908 meets the prominent Viennese architect Adolf Loos, who, having been impressed by one of the young artist's early paintings, takes an active interest in him.
Like Kokoschka, Loos rejects the prevailing decorative ideal, and he enthusiastically launches Kokoschka's artistic career by introducing him to sympathetic artists, securing him commissions for paintings, and providing him with much-needed spiritual inspiration and support.
Kokoschka during this early period paints mostly landscapes, developing a technique of vibrant, fluid lines and colors expressive of mood that form the basis for all of his subsequent paintings.
Kokoschka's landscapes at first glance seem to follow the principles of the Impressionist school because of their bright colors, ephemeral delineation of shapes, with tangled, multicolored lines, and preoccupation with light.
His vision, however, is different from that of the Impressionists, who sought, albeit in a revolutionary way, to represent only what struck the eye.
Die Brücke, manifesting the growing Expressionist movement, has grown to include Nolde, van Dongen, Max Pechstein, Otto Müller, the Swiss artist Cuno Amiet and the Finnish Symbolist Akseli Gallén-Kallela.
The paintings and prints by Die Brücke artists encompass all varieties of subject matter—the human figure, landscape, portraiture, still life—executed in a simplified style that stresses bold outlines and strong color planes, influenced by Primitivism.
Kirchner and Heckel are influenced by African and Pacific island art that they have seen in the Dresden ethnological museum; this Primitivism becomes an important element in Die Brücke style.
Manifestations of angst, or anxiety, appear in varying degrees in the works of Die Brücke painters and generally distinguish their art from that of the French Fauvists, who also are indebted to primitive art but who treat form and color in a more lyrical manner.
Die Brücke art is also deeply influenced by the expressive simplifications of late German Gothic woodcuts and by Munch's prints.
Kirchner's studies of the nude, such as Bathers at Moritzburg (1908;Tate Gallery, London), are often explicitly erotic, and in his lithograph Head of a Man with a Nude (1908), his fantasy of sexual aggression reaches nightmare intensity, but his worldly subjects represent only one aspect of the group; Nolde's earthy Primitivism of and Schmidt-Rottluff's emphatic pictorial rhetoric are more typical.
Both Nolde and Pechstein travel to the Pacific, but Nolde, a solitary and intuitive painter, after belonging for a year and a half dissociates himself from the tightly knit group.
In 1908, German physical chemist Fritz Haber develops, with Carl Bosch, a process for extracting nitrogen from air and production of ammonia for use as a fertilizer.
In 1907, French chemist Georges Urbain demonstrates that Marignac's earth is composed of two oxides, which Urbain calls lutecia and neoytterbia.
Around the same time, Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach independently discovers these elements and calls them cassiopeium and aldebaranium.
Urbain describes a process for separating lutecia from Marignac's ytterbia, and is credited with the discovery of a new element, which he names lutetium after Latin Lutetia, the ancient Roman name for his native city of Paris.
Austrian chemist and engineer Carl Auer von Welsbach, working independently, discovers the same element in 1908, and calls it cassiopeium.
The name lutetium becomes widely accepted, except in Germany, where it is commonly called cassiopeium until the 1950s.