Near East (2,637 – 910 BCE) …
Years: 2637BCE - 910BCE
Near East (2,637 – 910 BCE) Bronze and Early Iron — Delta Kingdoms, Aegean City-Coasts, Arabian Caravan Seeds
Geographic and Environmental Context
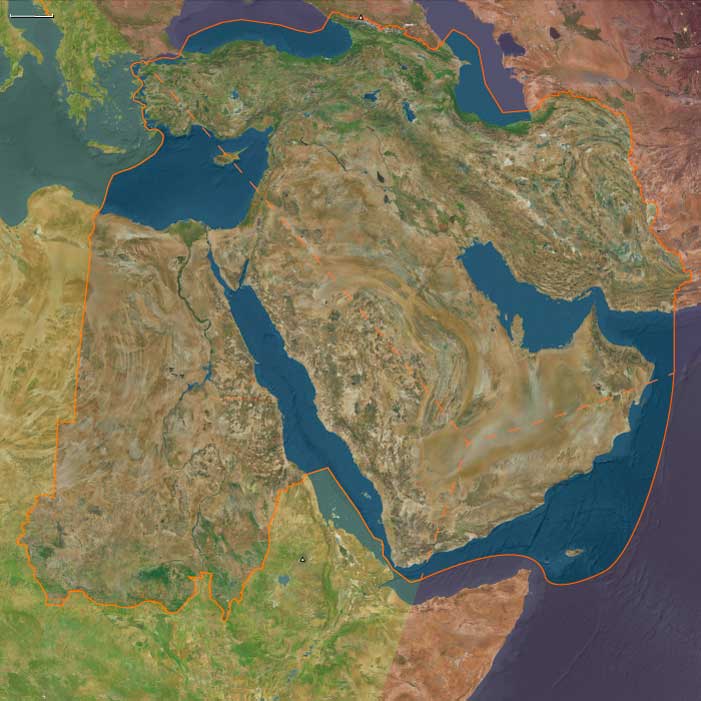
The Near East includes Egypt, Sudan, Israel, most of Jordan, western Saudi Arabia, western Yemen, southwestern Cyprus, and western Turkey (Aeolis, Ionia, Doris, Lydia, Caria, Lycia, Troas) plus Tyre (extreme SW Lebanon).-
Anchors: the Nile Valley and Delta; Sinai–Negev–Arabah; the southern Levant (with Tyre as the sole Levantine node in this subregion); Hejaz–Asir–Tihāma on the Red Sea; Yemen’s western uplands/coast; southwestern Cyprus; western Anatolian littoral (Smyrna–Ephesus–Miletus–Halicarnassus–Xanthos; Troad).
Climate & Environment
-
Nile floods oscillated; Aegean coastal plains fertile; Arabian west slope aridity increased, highland terraces scaled slowly.
Societies & Settlement
-
Lower/Upper Egypt (full Pharaonic cores just south but contiguous influence); Aegean Anatolia (Minoan/Mycenaean interactions; later Aeolian/Ionian/Dorian successors).
-
Levantine Tyre (within this subregion) arose as Phoenician node; Arabian west oases supported caravan precursors; Yemen west highlands nurtured terrace farming and incense beginnings.
Technology
-
Bronze widespread; early iron in Anatolia/Levant; sail-powered shipping matured; terracing and cisterns in Hejaz–Yemen highlands.
Corridors
-
Nile–Delta–Aegean maritime bridge; Tyre connected to Cyprus/Anatolia; Red Sea coastal cabotage began; Incense path seeds in Yemen–Hejaz.
Symbolism
-
Egyptian temple cosmology radiated north; Aegean cults at capes; Tyrian Melqart/Asherah; Arabian highland local cults.
Adaptation
-
Floodplain–coastal–terrace redundancy stabilized economies; incense gardens hedged aridity.
People
Groups
- Polytheism (“paganism”)
- Minoan (Cretan) culture, Early
- Kushitic Civilization
- Egypt (Ancient), Old Kingdom of
- Cyprus, Archaic
- Greece, archaic
- Canaanite culture, ancient
- Anatolia, archaic
- Nubian culture, ancient
- Kerma, Kingdom of
- Egypt (Ancient), First Intermediate Period of
- Minoan (Cretan) culture, Middle
- Hittites
- Egypt (Ancient), Middle Kingdom of
- Ugarit, Kingdom of
- Carians
- Assyria, vassal states of
- Egypt (Ancient), Second Intermediate Period of
- Hittites, (Old) Kingdom of the
- Phoenicia
- Minoan (Cretan) culture, Late
- Egypt (Ancient), New Kingdom of
- Hittites (Middle) Kingdom of the
- Arzawa
- Phoenicians
- Hittites (Hittite Empire), (New) Kingdom of the
- Assyria, (Middle) Kingdom of
- Tyre, Kingdom of (Phoenicia)
- Edomites, Kingdom of the
- Moabites, Kingdom of the
- Ammonites, Kingdom of the
- Sea Peoples
- Dorians
- Minaean Kingdom
- Ionians
- Lydia, Kingdom of
- Philistines
- Syro-Hittite states
- Lycia
- Egypt (Ancient), Third Intermediate Period of
- Priene, Greek City-State of
- Miletus (Ionian Greek) city-state of
- Judah, Kingdom of
- Israel (Northern Kingdom of)
- Assyria, (New) Kingdom of (Neo-Assyrian Empire)
Topics
- Early Bronze Age III (Near and Middle East)
- Early Bronze Age IV (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age I (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age II A (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age II B (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age II C (Near and Middle East)
- Late Bronze Age I and II A (Near and Middle East)
- Late Bronze Age III (Near and Middle East
- Kadesh, Battle of
- Bronze Age collapse
- Iron Age, Near and Middle East
Commodoties
- Rocks, sand, and gravel
- Weapons
- Hides and feathers
- Gem materials
- Glass
- Colorants
- Domestic animals
- Grains and produce
- Textiles
- Ceramics
- Strategic metals
- Lumber
- Industrial chemicals
- Aroma compounds
Subjects
- Commerce
- Symbols
- Writing
- Architecture
- Watercraft
- Sculpture
- Painting and Drawing
- Environment
- Decorative arts
- Faith
- Government
- Custom and Law
- Mathematics
- Human Migration
- Medicine
- Horology
- Metallurgy