The Middle East (1684–1827 CE): Ottoman Decline, …
Years: 1684 - 1827
The Middle East (1684–1827 CE): Ottoman Decline, Safavid Collapse, and the Rise of New Powers
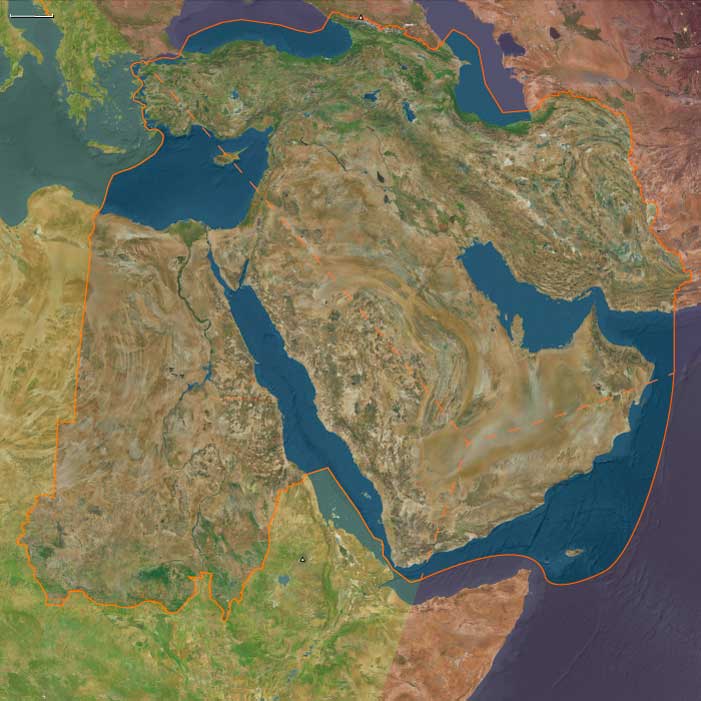
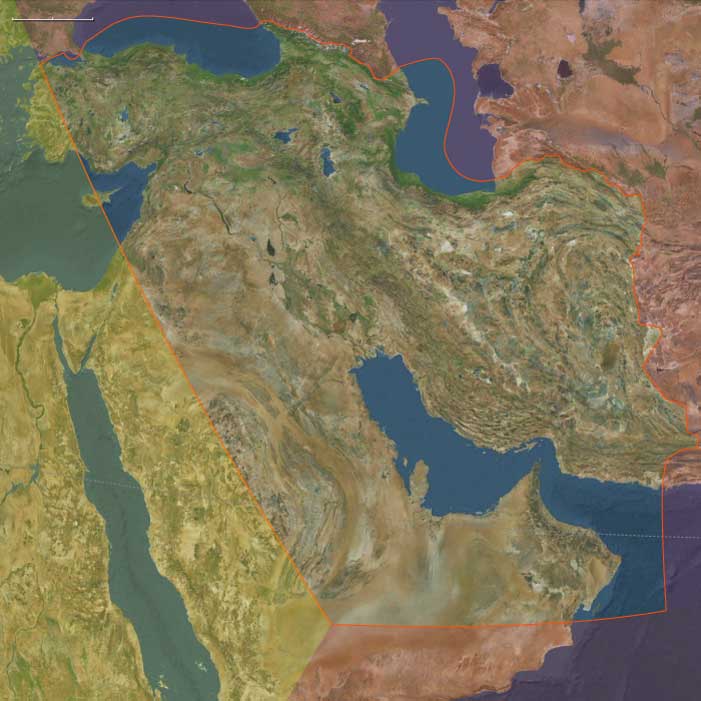
Geography & Environmental Context
The Middle East includes Iraq, Iran, Syria, Armenia, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Qatar, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, most of Turkey (except the European part and southwest Anatolia), eastern Jordan, all but southernmost Lebanon, eastern Saudi Arabia, and northern Oman. Anchors include the Tigris–Euphrates basin (Mesopotamia), the Zagros and Caucasus ranges, the Iranian Plateau, the Caspian littoral, the Syrian Desert, and the Persian Gulf and Caspian Sea coasts. This geography spans irrigated river valleys, steppe corridors, semi-arid plateaus, and mountain enclaves linking Anatolia, Persia, and Arabia.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
The period fell within the late Little Ice Age, producing cooler winters in Anatolia, Armenia, and the Caucasus, alongside recurrent droughts in Mesopotamia and Iran. Floods along the Tigris and Euphrates periodically devastated farmlands, while earthquakes struck Tabriz (1721) and Shiraz (1824). Pastoral nomads in Arabia, Iran, and the Caucasus moved widely to buffer drought, while irrigation in Mesopotamia and northern Iran faltered under war and neglect but revived when political stability returned.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Mesopotamia: Date groves, rice paddies, and cereal fields along the Tigris–Euphrates remained staples; tribal confederations dominated countryside around Ottoman Baghdad.
-
Iranian Plateau: Dryland farming (wheat, barley) and oasis gardening (fruit, melons) sustained populations; silk in Gilan and rice in Mazandaran anchored Caspian subsistence.
-
Caucasus (Armenia, Georgia, Azerbaijan): Pastoralism, viticulture, and orchards flourished in upland valleys; caravan towns like Tiflis and Yerevan mediated exchange.
-
Anatolia & Syria: Grain, olives, and vines in uplands; Aleppo and Damascus remained provisioning and craft centers despite periodic crises.
-
Persian Gulf & Oman: Fishing, date cultivation, and pearling dominated, with maritime trade sustaining settlements from Basra to Muscat.
Technology & Material Culture
Agriculture relied on qanats, canals, and animal-powered irrigation. Fortresses and caravanserais dotted plateau routes; mosques, madrasas, and Armenian and Georgian churches anchored towns. Persian silk textiles, Azerbaijani carpets, and Aleppine cottons were prized. Gunpowder weapons, artillery, and fortress improvements spread, though unevenly. Maritime craft ranged from Ottoman galleys to Omani dhows controlling Indian Ocean lanes.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Caravan routes: Linked Aleppo to Mosul and Baghdad; Isfahan to Tabriz, Yerevan, and Baku; Basra to the Gulf; Shiraz and Yazd to Hormuz/Muscat.
-
Persian Gulf: Omani seafaring extended across the Arabian Sea; Basra exported dates and grain; pearl fisheries tied Bahrain and Qatar to Indian and European markets.
-
Caspian trade: Connected Gilan’s silk and Astrakhan’s markets; Russian expansion brought new garrisons and merchants.
-
Imperial contest zones: Anatolia and the Caucasus saw repeated wars; Iraq oscillated between Ottoman and Persian control.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ottoman provinces: Islam anchored society through mosques, Sufi lodges, and guilds; Armenian and Syriac Christians maintained schools and churches; Jewish communities thrived in Aleppo and Baghdad.
-
Safavid Iran: Shi‘ism remained state religion; Isfahan’s mosques and gardens expressed grandeur, though after the Safavid collapse, Qajar art and architecture reshaped Persian identity.
-
Caucasus: Christian Orthodoxy (Georgian, Armenian) coexisted with Islam; mountain oral epics and shrine pilgrimages preserved memory.
-
Arabian littoral: Tribal poetry, pearl-diver songs, and Omani mosque schools expressed maritime identity.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Nomadic strategies: Tribal migrations across steppe and desert balanced drought and grazing.
-
Oasis and qanat systems: Managed water for cereals and orchards; local repair after war was critical.
-
Silk, carpet, and date economies: Offered export resilience when crops failed.
-
Maritime trade: Oman and Gulf ports buffered against inland disruption by maintaining Indian Ocean routes.
Transition
Between 1684 and 1827, the Middle East was a contested imperial borderland. The Safavid dynasty collapsed (1722); Afghans, Ottomans, and Russians fought over Iran and the Caucasus. Nader Shah briefly restored Persian power (1736–1747), raiding into India and the Caucasus. The Qajar dynasty (from 1794) consolidated Iran but conceded land to Russia in treaties (Gulistan 1813, Turkmenchay 1828). The Ottoman Empire faced Russian expansion in the Black Sea and Caucasus and Wahhabi revolts in Arabia. Oman emerged as a naval power, dominating the Gulf and East Africa. By 1827, the region was still a mosaic of caravans, mosques, and fortified towns, but the balance of power had tilted toward European and Russian pressures—foreshadowing the 19th-century age of colonial rivalry and reform.
People
- Abdullah bin Saud
- Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar
- Ahmad bin Said al-Busaidi
- Alexander I of Russia
- Bashir Shihab II
- Dawūd Pasha
- Fath-Ali Shah Qajar
- Heraclius II of Georgia
- Karim Khan Zand
- Mohammad Hasan Khan Qajar
- Muhammad Ali of Egypt
- Muhammad bin Saud
- Muhammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhab
- Nader Shah
- Said bin Sultan
- Sulayman the Great
- Suleiman I of Persia
- Sultan Husayn
- Turki bin Abdullah bin Muhammad
Groups
- Georgians
- Armenian people
- Jews
- Christians, Armenian Apostolic Orthodox
- Christians, Maronite
- Muslims, Sunni
- Muslims, Shi'a
- Muslims, Ibadi
- Oman, First Imamate of
- Ottoman Empire
- Imeriti, Kingdom of
- Kakheti, Kingdom of
- Persia, Safavid Kingdom of
- Mount Lebanon Emirate
- Egypt, Ottoman eyalet of
- Russia, Tsardom of
- Cyprus, Ottoman
- Yaruba dynasty
- Thani, House of
- Omani Empire
- Al Qasimi (Adnani Arabian tribe)
- Al Khalifa family
- Britain, Kingdom of Great
- Russian Empire
- Persia, Hotaki Ghilzaid Kingdom of
- Wahhabism
- Persia, Afsharid Kingdom of
- Persia, Zandid Kingdom of
- Kuwait, Sheikhdom of
- Kartli-Kakheti, Kingdom of
- Saud, House of
- Persia, Qajarid Kingdom of
- Georgia within the Russian Empire
- Britain (United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland)
- Egypt, (Ottoman) Viceroyalty of