Southeast Arabia (2,637 – 910 BCE) …
Years: 2637BCE - 910BCE
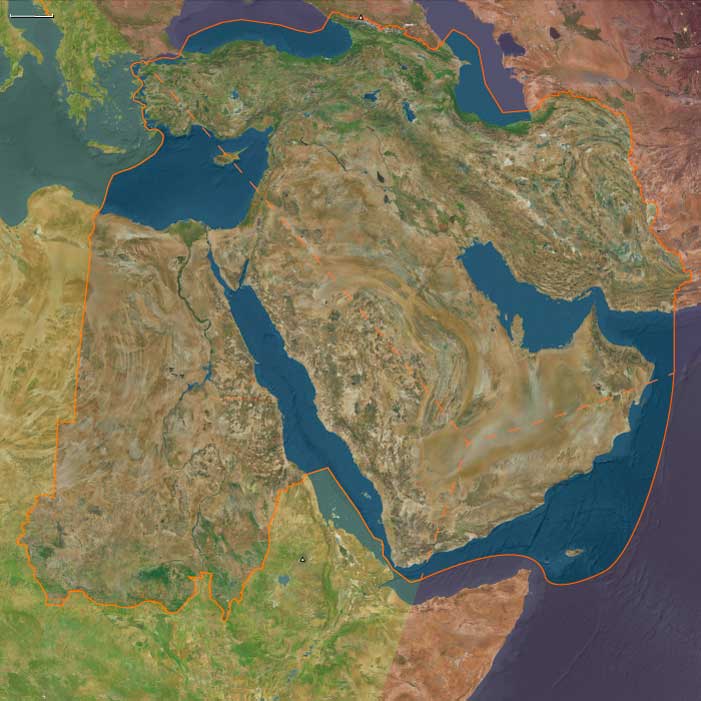
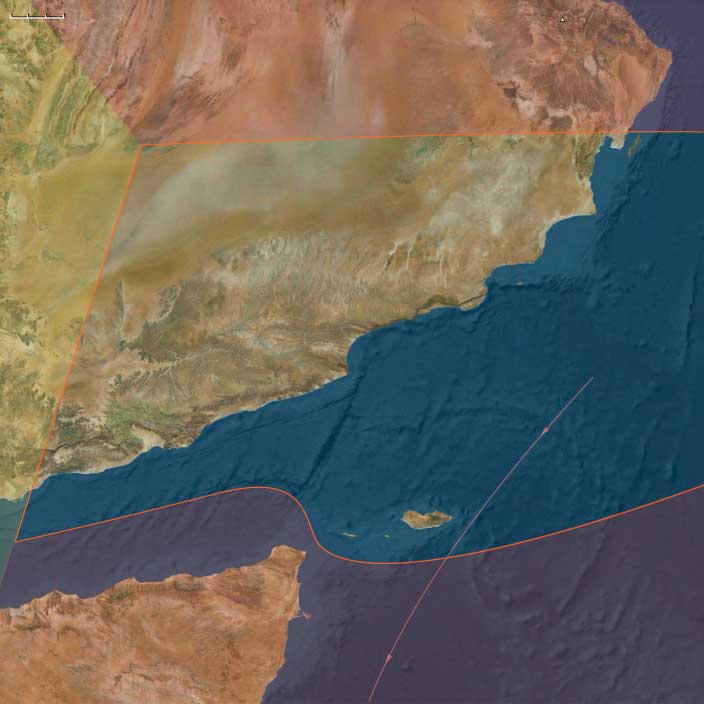
Southeast Arabia (2,637 – 910 BCE) Bronze and Early Iron — Incense, Pastures, and Canoe Hubs
Geographic and Environmental Context
Southeast Arabia covers the southern and eastern margins of the Arabian Peninsula:-
Eastern Yemen (Hadhramaut, eastern Aden interior, al-Mahra).
-
Southern Oman (Dhofar Highlands with the khareef monsoon, al-Wusta gravel plains, Sharqiyah Desert fringes).
-
The Empty Quarter (Rubʿ al-Khālī) margins in adjoining Saudi territory.
-
The offshore island of Socotra in the Arabian Sea.
-
Anchors: Wādī Ḥaḍramawt–Shibam–Tarim, Dhofar escarpments (Ẓafār/Al-Balīd, Mirbat), al-Mahra dunes, al-Wusta plains, Sharqiyah sands, Socotra’s Hagghier Mountains and dragon’s-blood groves.
-
Dhofar terraces, Hadhramaut wadis, Socotra.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Increasing aridification; terraces and fog-belt stability buffered upland.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Terrace horticulture of millet, dates, tubers; goat/camel pastoralism.
-
Resin harvesting expanded.
-
Maritime dried-fish economies.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Bronze tools; iron appears late.
-
Sewn-plank dhows; cisterns.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Incense moved north to Yemen; Socotra resin/aloe exported; Gulf links.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ritual incense burning; ancestor tombs.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Resilient trinity: terrace, herd, incense, fish.
Transition
By 910 BCE, incense trade tied Southeast Arabia to broader West Asian exchange.
Topics
- Early Bronze Age III (Near and Middle East)
- Abrolhos Transgression
- Early Bronze Age IV (Near and Middle East)
- 4.2 kiloyear BP aridification event
- Middle Bronze Age I (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age II A (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age II B (Near and Middle East)
- Middle Bronze Age II C (Near and Middle East)
- Late Bronze Age I and II A (Near and Middle East)
- Late Bronze Age III (Near and Middle East