Northwestern North America (2,637 – 910 BCE) …
Years: 2637BCE - 910BCE
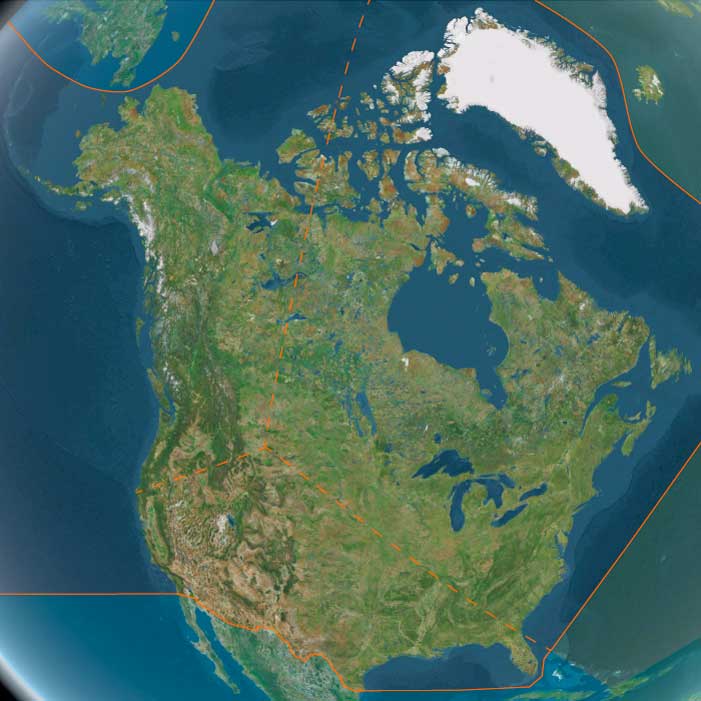
Northwestern North America (2,637 – 910 BCE) Metal Elsewhere, Copper & Slate Here — ASTt in the Arctic, Ranked Households on the Coast
Geographic and Environmental Context
Northwestern North America includes Alaska, western Canada (Alberta, British Columbia, Yukon and Northwest territory and Nunavut west of 110°W) Alaska, Washington State, northern Idaho, and the northwestern portions of Montana, Oregon, and California.
-
Anchors: Western Arctic Alaska (Kotzebue Sound–Norton Sound), Brooks Range, Cook Inlet–Prince William Sound, Haida Gwaii–Central Coast, Fraser–Columbia plateaus.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Gradual cooling; reliable salmon cycles continued; sea-ice dynamics shaped Arctic foraging.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
In the western Arctic, the Arctic Small Tool tradition (ASTt) (c. 2500–800 BCE) established small, mobile camps with microblades and finely made points—precursors to later Paleo-Inuit and Thule systems.
-
Along the North Pacific Coast, ranked households with large plank dwellings consolidated control of weirs, canoe landings, and cedar groves; interior pit-house towns persisted.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Native copper (NW Alaska/Interior) cold-hammered into awls, points; ground slate knives/weapons proliferated on coasts.
-
Oil lamps, skin-covered boats in Arctic; heavy carpentry tools on coasts; labrets appear variably around Gulf of Alaska contexts.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Grease trails (eulachon oil) from inlets to interior; obsidian (Edziza) widely traded; Arctic driftwood routes supplied interior treelines.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Salmon and sea-mammal rituals matured; clan or crest-like identifiers emerged in house art and grave goods in some coastal zones.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Storage economies plus multi-ecozone mobility buffered climatic variability; copper/slate innovations improved cutting and sewing in wet–cold conditions.
Transition
On the eve of the 1st millennium BCE, the region juxtaposed mobile Arctic microlithic traditions with coastal ranked house societies and interior villages bound by grease and obsidian trails.
Groups
- Kwakwakaʼwakw
- Haida people
- Tlingit people
- Athabaskans, or Dene, peoples
- Klamath (Amerind tribe)
- Tsimshian
- Aleutian Tradition
Topics
- Archaic Stage (Americas)
- Subboreal Period
- Abrolhos Transgression
- 4.2 kiloyear BP aridification event
- Formative Stage (Americas)
- Rottnest Transgression
- Younger Subboreal Period