Northwest Asia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper …
Years: 28577BCE - 7822BCE
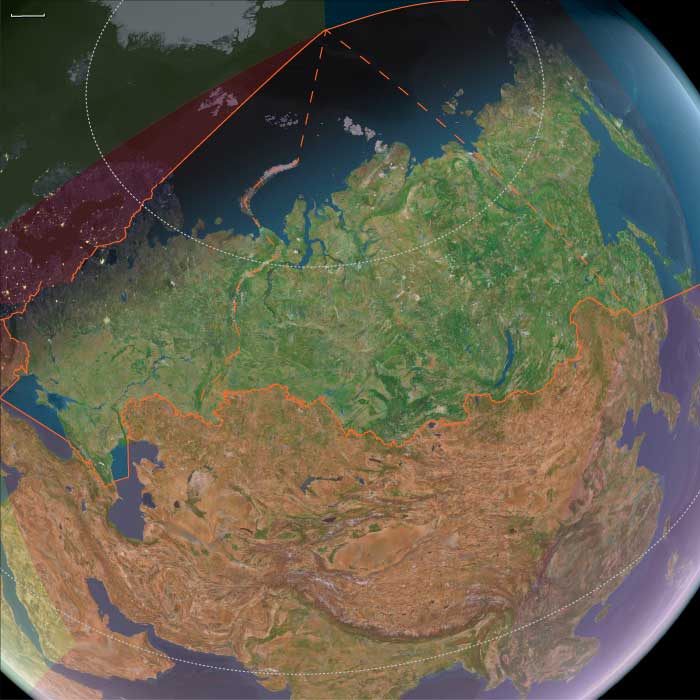
Northwest Asia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper Pleistocene II — Deglaciation, Forest Advance, and Lake Highstands
Geographic and Environmental Context
Northwest Asia includes the lands from the Ural Mountains east to ~130°E, encompassing Western and Central Siberia.
-
Anchors: Ob floodplains, Altai piedmont lakes, Yenisei–Minusinsk Basin, Ural passes.
-
Deglaciation created large pluvial lakes in the Altai and Minusinsk depressions.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød warming improved rainfall and forest belts; Younger Dryas reversed conditions briefly; Early Holocene warmth stabilized environments.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Diets diversified: elk, reindeer, beaver, fish, nuts, and berries.
-
Semi-sedentary lakeside camps emerged around pluvial lakes and Ob–Yenisei channels.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Microblade complexes persisted; ground-stone tools for plant processing began; bone harpoons and fishing gear.
-
Ornaments in antler, amber, and imported shells.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Ob–Irtysh trunklines enabled north–south mobility; Altai passes linked into Central Asia; Ural passes tied to European plains.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ritual deposits at lakesides; ochre burials continued; petroglyphs began in Minusinsk–Altai zones.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Broad-spectrum foraging buffered climatic reversals; canoe precursors and rafts likely aided mobility on large lakes.