Northern South Atlantic (1972–Present): Strategic Shifts, Conservation, …
Years: 1972 - 2215
Northern South Atlantic (1972–Present): Strategic Shifts, Conservation, and the Pursuit of Sustainability
Ascension Island: Strategic Evolution and Technological Expansion
From the 1970s onward, Ascension Island consolidates its critical role as a strategic communications and military installation. The island's significance peaks during the Falklands War (1982) when the British military leverages the Wideawake Airfield as a vital staging point for aircraft deploying to the South Atlantic conflict zone. The strategic value demonstrated during this conflict strengthens Ascension’s geopolitical prominence.
Throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries, Ascension continues to serve as an essential node in global communications and military infrastructure. Advanced satellite tracking and telemetry facilities support international space exploration and monitoring programs, most notably those operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), NASA, and the U.S. Air Force. High-tech installations like the BBC Atlantic Relay Station, established to broadcast radio transmissions into Africa and South America, further enhance Ascension's international relevance.
In recent decades, Ascension's governance evolves toward greater civilian participation. A small, diverse resident population develops, characterized by unique legal and social frameworks designed to balance civilian life with the island’s strategic military functions. However, permanent residency rights and self-determination remain ongoing issues, as most inhabitants remain temporary contract workers, highlighting the island's continued ambiguity between military use and civil society aspirations.
St. Helena: Isolation, Economic Revival, and Connectivity
Since the late 20th century, St. Helena grapples continuously with economic stagnation due to geographic isolation. Persistent emigration, primarily toward the UK, South Africa, and the Falkland Islands, exacerbates demographic pressures and contributes to labor shortages. The island’s reliance on British financial aid remains pronounced, though gradual efforts to diversify the local economy begin to take hold in the 21st century.
Efforts to improve global connectivity culminate with the construction and eventual opening of St. Helena Airport in 2016. Despite initial setbacks—including wind-shear problems limiting large aircraft access—the airport marks a significant shift toward economic self-sufficiency, promoting tourism, facilitating faster travel, and enabling increased investment opportunities. The new infrastructure is envisioned as a catalyst for economic revitalization, potentially ending centuries of acute geographic isolation.
Governance on St. Helena advances significantly during this period, with the island achieving greater administrative autonomy through enhanced democratic structures, including expanded local councils, ministerial systems, and public participation. Education, healthcare, and environmental sustainability become focal points for development policies, reflecting broader trends toward social progress and self-governance.
Conservation Initiatives and Ecological Restoration
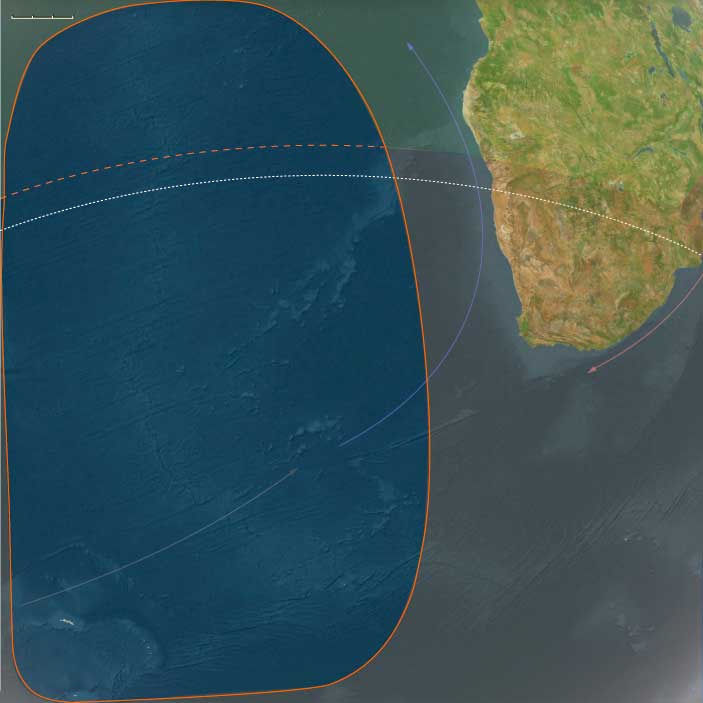
Beginning in the 1980s and intensifying into the 21st century, both islands witness a growing awareness of environmental challenges, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable development. Ascension Island Marine Protected Area (MPA), established in 2019, covers 100% of Ascension's Exclusive Economic Zone, becoming one of the world's largest marine reserves. These efforts seek to protect critical habitats, including breeding grounds for endangered species like green turtles and nesting sites for seabirds.
Similarly, St. Helena establishes its own Marine Protected Area in 2016, significantly safeguarding local marine biodiversity. Both islands pursue aggressive conservation policies aimed at reversing environmental degradation caused by historic human activity, promoting reforestation, protecting endemic species, and fostering sustainable fishing and eco-tourism.
Geopolitical Importance in the 21st Century
Ascension’s geopolitical role continues to evolve amid renewed global strategic competition, especially between Western powers and emerging global actors. The island serves as a key asset for intelligence, surveillance, and global communications, underscoring its enduring strategic value within British and international military and diplomatic networks.
St. Helena, by contrast, positions itself as a peaceful haven promoting eco-tourism, scientific research, and historical tourism, notably around Napoleonic heritage sites. The island seeks stronger economic ties through partnerships in science and education, aiming to mitigate the vulnerabilities inherent to small island communities.
Legacy of the Age
The period from 1972 to the present marks a transformative chapter for both Ascension Island and St. Helena. Ascension has solidified its position as an essential strategic and communications nexus, intricately woven into global technological and geopolitical networks. Conversely, St. Helena has progressively overcome historical isolation, leveraging improved connectivity and economic diversification to enhance sustainability and local governance. Both islands, through proactive conservation efforts and policy innovations, illustrate broader global themes of strategic geopolitics, environmental sustainability, and evolving local identity in the face of changing global circumstances.