Mediterranean West Europe (909 BCE – CE …
Years: 909BCE - 819
Mediterranean West Europe (909 BCE – CE 819): Coastal Strongholds, Mountain Valleys, and Frankish–Iberian Frontiers
Geographic and Environmental Context
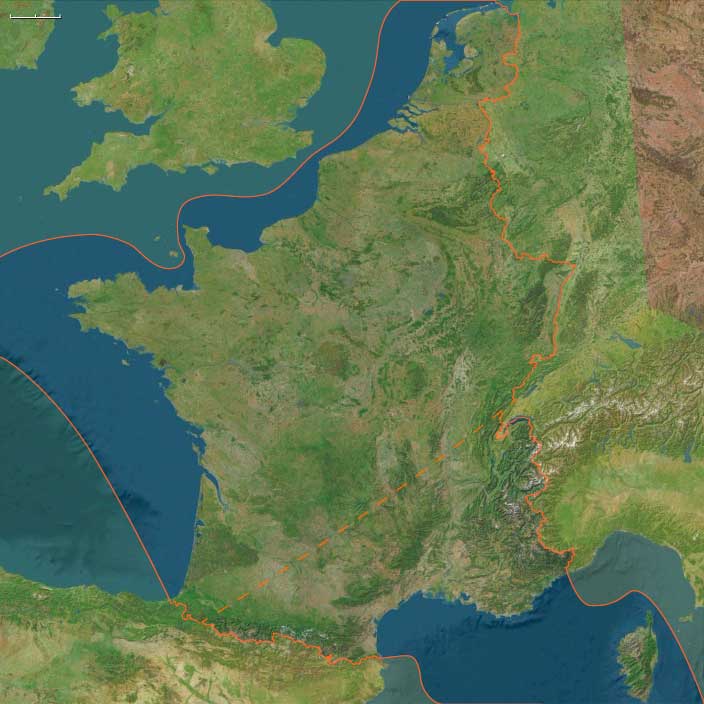
Mediterranean West Europe includes southern France, Monaco, and Corsica.
-
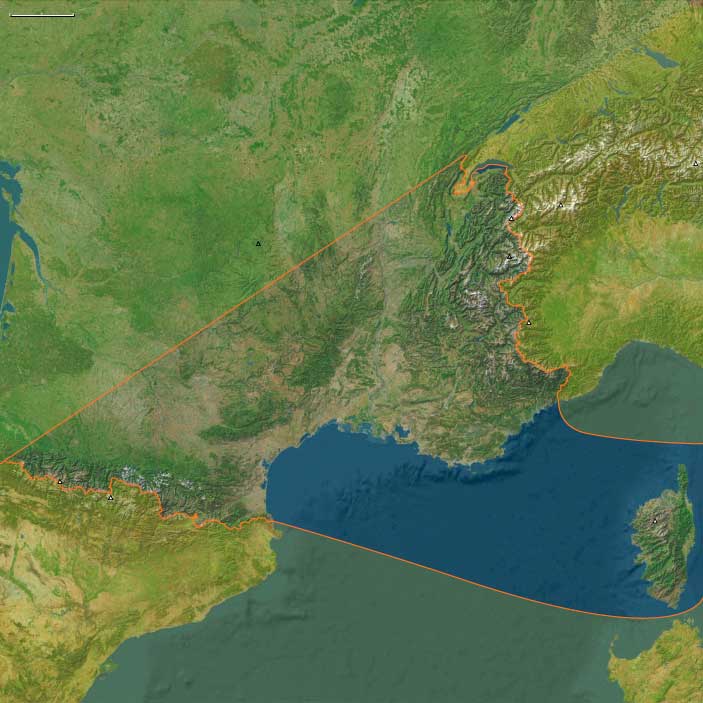
The subregion encompasses the French Pyrenees, the Languedoc-Roussillon and Provence coasts, the Rhone Valley, and the rugged island interior of Corsica.
-
Its Mediterranean shoreline features natural harbors, while inland valleys connect to the Alps and Atlantic West Europe.
Climate and Environmental Shifts
-
A Mediterranean climate with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers favored vineyards, olive groves, and grain cultivation.
-
Seasonal droughts in lowlands and occasional flooding in river valleys required adaptive agricultural practices.
-
Upland pastures supported transhumant herding.
Societies and Political Developments
-
Much of the mainland coast and the Rhone Valley were integrated into the Frankish realms, with Marseille and Arles serving as key trade and administrative centers.
-
The Pyrenean frontier was contested between the Franks and the Umayyad forces in Iberia, giving rise to buffer zones like the Marca Hispanica.
-
Corsica experienced shifting control between the Byzantine Empire and Lombard or Frankish influence, with local communities maintaining considerable autonomy.
Economy and Trade
-
Agricultural production included wine, olive oil, grain, and pastoral products from uplands.
-
The Rhone River facilitated trade between the Mediterranean coast and inland markets in West Central Europe.
-
Coastal ports handled goods such as ceramics, textiles, spices, and metalware, linking the subregion to Italy, North Africa, and the wider Mediterranean.
-
Salt production along parts of the coast supplied both local needs and export markets.
Subsistence and Technology
-
Irrigation canals and terrace farming techniques maximized agricultural output in arid zones.
-
Shipbuilding supported both coastal navigation and longer voyages across the western Mediterranean.
-
Milling technology, including water mills, was used for grain processing.
Movement and Interaction Corridors
-
Maritime routes connected Marseille, Nice, and Corsican ports to Italy, Iberia, and North Africa.
-
Land routes through the Rhone Valley linked the Mediterranean coast to transalpine passes.
-
The Pyrenean passes provided channels for trade and military movement between Frankish Gaul and Iberia.
Belief and Symbolism
-
Christianity was dominant, with bishoprics and monasteries active in both urban and rural areas.
-
Monastic centers preserved classical texts and advanced the Carolingian cultural revival.
-
Church architecture combined Roman and local traditions, often featuring early medieval stone carving.
Adaptation and Resilience
-
Coastal and inland economic diversity reduced vulnerability to poor harvests or maritime disruptions.
-
Fortifications protected against seaborne raids and frontier incursions.
-
Strategic control of river valleys and mountain passes ensured economic and political influence.
Long-Term Significance
By CE 819, Mediterranean West Europe was a strategic bridge between the Frankish heartlands and the Mediterranean world, economically tied to long-distance trade and politically shaped by its frontier position with Islamic Iberia.
Groups
- Corsica et Sardinia (Roman province)
- Christianity, Chalcedonian
- Corsica, Medieval
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Leonid dynasty
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Justinian dynasty
- Lombards (Italy), Kingdom of the
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Heraclian dynasty
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Heraclian dynasty
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Isaurian dynasty
- Francia (Carolingians)
- Córdoba, Umayyad Emirate of
- Italy, Carolingian Kingdom of
- Marca Hispanica
- Frankish, or Carolingian (Roman) Empire
Commodoties
- Weapons
- Domestic animals
- Grains and produce
- Textiles
- Ceramics
- Strategic metals
- Salt
- Beer, wine, and spirits
- Manufactured goods
- Spices