Following Germany’s renewal of unrestricted submarine warfare in early 1917, Wilson asks Congress in April for a declaration of war, urging that “the world must be made safe for democracy.” The US Congress assents.
The US Congress passes the Trading with the Enemy Act of 1917, which forbids US firms or their foreign sudsidiaries from trading with enemies of the United States except under license.
The US Congress passes the Espionage Act of 1917.
The US Congress passes the Invention Secrecy Act of 1917 as a wartime measure to prevent disclosure of inventions that "might be detrimental to the public safety or defense.”
Wilson, seeking and receiving legislative delegation of increased powers, immediately establishes a series of war agencies to extend federal control over industry, transportation, labor, food, fuel, and prices.
In May, Wilson rams a Selective Service bill through Congress.
Supporters of the Harrison Act fail in a 1917 attempt to force drug control regulation on Coca-Cola, which employs cocaine as a key ingredient in its secret recipe
The government closes the U. S. Navy’s German-built radio station on Mystic Island in 1917.
In the August 1917 issue of The Experimenter, Tesla describes the invention of radar.
Tesla has reportedly achieved a charge of 20 million volts in some of his devices.
He reluctantly accepts the “Edison Medal” in 1917.
William Wirt, in 1917, brings the Carnegie Institution’s schooling system to twelve predominantly Jewish New York City schools.
Jewish immigrants, realizing what is being perpetrated, riot for three weeks.
Over 200 school children are jailed.
Trotsky arrives in New York in 1917 aboard the steamer Montserrat and allegedly receives funds for the planned revolution in Russi, to which he returns.
J. P. Morgan, Jr. is instrumental in financing $1.5 billion in Allied military purchases during the Great War.
New Thought lecturer David Van Bush hires H.P.
Lovecraft as a ghost writer.
As of 1917, fifteen states in the US have eugenics legislation that authorizes sterilization of criminals, epileptics, the retarded and the insane.
The Bluemont, Virginia site purchased in 1903 by the US is used during the Great War as an artillery range.
The 1917 entry of America into the war tips the balance in favor of the Allies.
The United States, upon its entry into the World War, passes the Selective Service Act.
Herbert Hoover is called to Washington to serve as food adminstrator, a special wartime office created to encourage American agricultural production and food conservation and to coordinate a rational distribution of food.
American financier Bernard M. Baruch, who began his career in a Wall Street brokerage house and made a fortune in stocks while still a young man, serves as chairman of the War Industries Board.
The AMA, in 1917, opposes compulsory health insurance.
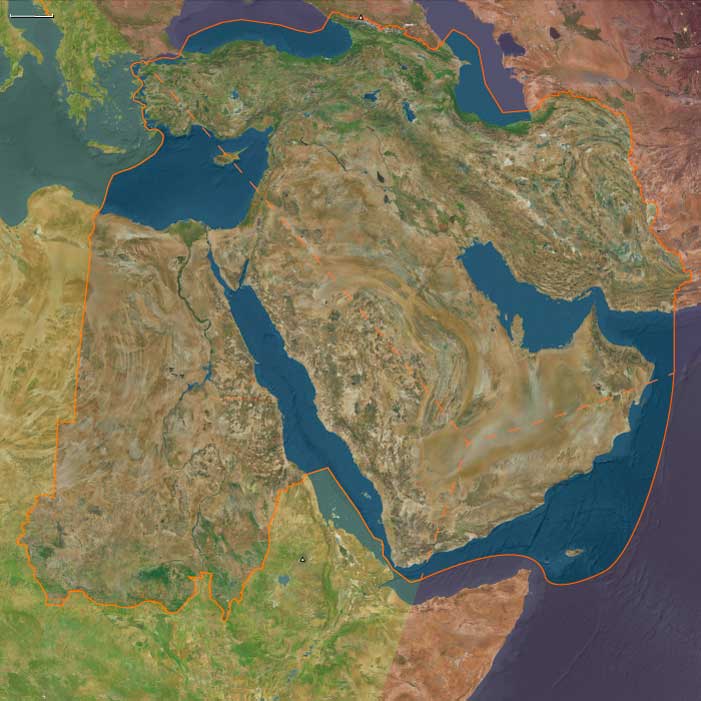
British government officials inform Lord Rothschild of the intent to establish a Jewish homeland in Palestine; the Zionist movement, which some allege to be a creation of British Intelligence, supports the plan.
The 1917 Balfour Declaration on the Jewish Homeland gains Jewish support for war efforts and sows the seeds for a Middle East "balance of power" card.
The British military employs phosgene gas-containing artillery shells against the German forces in 1917.
Wartime stockpiles of chlorine are allegedly designated for use in post-war water supplies.
X-ray methodology ascertains atomic numbers.
In 1917, Norman Thomas, a pacifist Presbyterian minister in East Harlem’s slums, helps to found what will become the American Civil Liberties Union.
Wilson, on January 8, 1918, presents his Fourteen Points, a comprehensive enumeration of his war aims that serves to inspire the Allies while undermining the confidence of the Germans.