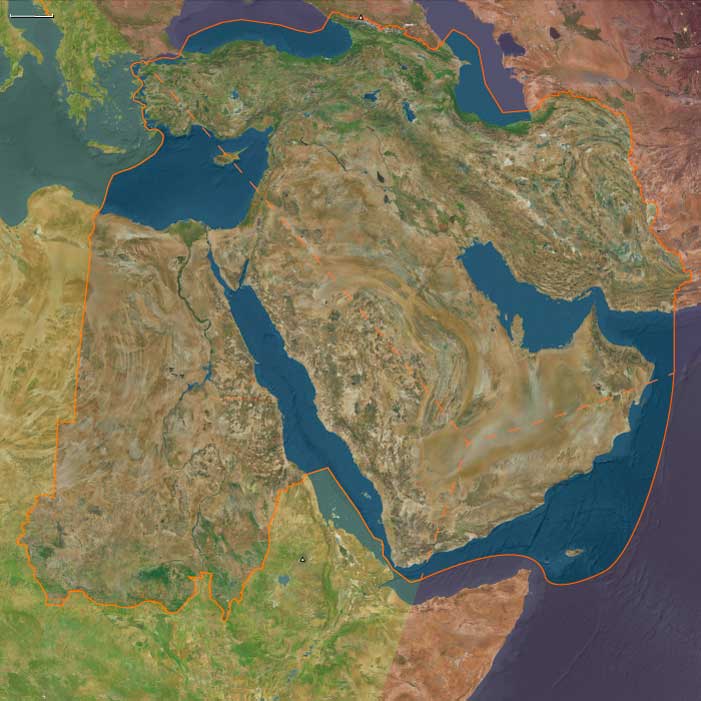
The small population of moderns had spread from the Near East to South Asia by fifty thousand years ago, and on to Australia by forty thousand years ago, Homo sapiens for the first time colonizing territory never reached by Homo erectus.
It has been estimated that from a population of two thousand to five thousand individuals in Africa, only a small group, possibly as few as one hundred and fifty to one thousand people, crossed the Red Sea.
Of all the lineages present in Africa only the female descendants of one lineage, mtDNA haplogroup L3, are found outside Africa.
Had there been several migrations one would expect descendants of more than one lineage to be found outside Africa.
L3's female descendants, the M and N haplogroup lineages, are found in very low frequencies in Africa (although haplogroup M1 is very ancient and diversified in North and Northeast Africa) and appear to be recent arrivals.
A possible explanation is that these mutations occurred in East Africa shortly before the exodus and, by the founder effect, became the dominant haplogroups after the exodus from Africa.
Alternatively, the mutations may have arisen shortly after the exodus from Africa.
Some genetic evidence points to migrations out of Africa along two routes.
However, other studies suggest that only a few people left Africa in a single migration that went on to populate the rest of the world, based in the fact that only descents of L3 are found outside Africa.
From that settlement, some others point to the possibility of several waves of expansion.