The Near East (28,577 – 7,822 …
Years: 28577BCE - 7822BCE
The Near East (28,577 – 7,822 BCE) Upper Pleistocene II — Bølling–Allerød Nile Bounty, Younger Dryas Stress, Early Holocene Recovery
Geographic and Environmental Context
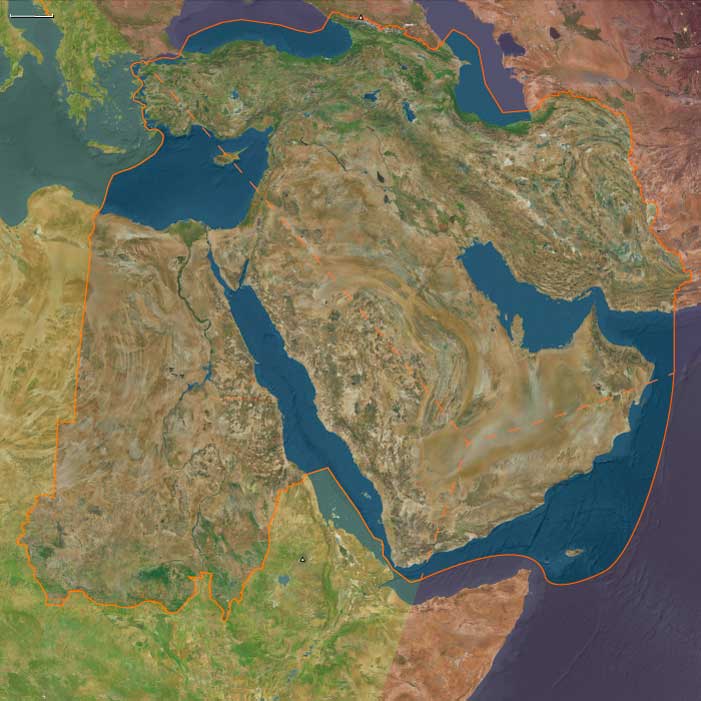
The Near East includes Egypt, Sudan, Israel, most of Jordan, western Saudi Arabia, western Yemen, southwestern Cyprus, and western Turkey (Aeolis, Ionia, Doris, Lydia, Caria, Lycia, Troas) plus Tyre (extreme SW Lebanon).-
Anchors: the Nile Valley and Delta; Sinai–Negev–Arabah; the southern Levant (with Tyre as the sole Levantine node in this subregion); Hejaz–Asir–Tihāma on the Red Sea; Yemen’s western uplands/coast; southwestern Cyprus; western Anatolian littoral (Smyrna–Ephesus–Miletus–Halicarnassus–Xanthos; Troad).
Climate & Environment
-
Bølling–Allerød: Nile floods more generous; Levantine–Aegean woodlands expanded.
-
Younger Dryas: aridity spike; Nile floods weakened; Early Holocene restored stability.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Intensified fish–fowl–reed economies in Nile; broad-spectrum foraging in Levant; shellfish and nearshore fish along Aegean Turkey; Red Sea relict mangroves used intermittently.
Technology
-
Microlithic composites; grinders/mortars for seeds; fishing gear (gorges, traps); early dugout/raft precursors.
Corridors
-
Nile remained the main artery; Sinai–Negev link; Ionia–Carian capes for seasonal forays.
Symbolism
-
Cemeteries at levee ridges; ritual disposal in dune/shore settings; persistent ochre.
Adaptation
-
Storage + wetland scheduling mitigated Younger Dryas volatility.
Groups
Topics
Commodoties
Subjects
Regions
Subregions
Related Events
Filter results
Showing 10 events out of 69584 total
The questions of how, when, and why the first peoples entered the Americas remain subjects of active research, though recent genomic advances have significantly refined our understanding. While there is general agreement that the Americas were first settled by peoples who migrated from Asia across Beringia, the migration patterns, timing, and genetic origins have proven far more complex than previously recognized.
Archaeological evidence suggests that widespread human habitation of the Americas occurred during the late glacial period (roughly 16,500-13,000 years ago), following the Last Glacial Maximum. However, sites like White Sands, New Mexico, suggest human presence as early as 21,000-23,000 years ago, potentially during the height of glaciation.
Whole-genome studies have revolutionized understanding of Native American origins, revealing that while most ancestry stems from a shared founding population, at least four distinct streams of Eurasian migration contributed to present-day and prehistoric Native American populations. Ancient DNA analysis of individuals like the 12,600-year-old Anzick-1 child (associated with Clovis artifacts) confirms genetic continuity between early inhabitants and modern Native Americans, contradicting theories of population replacement.
Current research supports a model involving initial migration from a structured Northeast Asian source population, followed by a period of isolation in Beringia, and subsequent coastal migration into the Americas. This founding population then diversified within the continent, splitting into northern and southern lineages around 14,500-17,000 years ago. Additionally, some Amazonian populations show genetic signatures suggesting ancestry from a second source related to indigenous Australasians, indicating an even more complex founding history.
Rather than simple single versus multiple migration models, the genetic evidence points to a nuanced process involving multiple ancestral streams, periods of isolation, rapid expansion, and subsequent diversification within the Americas.
Southeast Indian Ocean (28,577–7,822 BCE): Ice Retreat and Expanding Shores
Geographic & Environmental Context
The subregion of Southeast Indian Ocean includes Kerguelen east of 70°E and Heard Island and McDonald Islands. Kerguelen’s eastern plateaus and fjord systems dominated the landscape, while Heard Island’s volcanic massif of Big Ben rose above glaciated coasts. The McDonald Islands remained small, rugged, and volcanically active, barely peeking above stormy seas.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
This epoch bridged the Last Glacial Maximum (c. 26,000–19,000 BCE) and the slow deglaciation that followed. Icefields on Kerguelen and Heard expanded dramatically at first, carving valleys and pushing tongues of ice toward the coasts. After 20,000 BCE, retreat began, revealing tundra and freshwater lakes. Sea levels gradually rose—by the end of the epoch, they had climbed tens of meters, re-drowning coastal shelves. The Southern Ocean warmed slightly, altering circulation and plankton blooms.
Subsistence & Settlement
Still uninhabited by humans, the islands were ecologically vibrant. Expanding tundra vegetation reclaimed glacial forelands. Migratory seabirds—especially penguins and petrels—flourished as new rookeries opened on ice-free coasts. Seal and sea lion populations rose in tandem with available haul-out sites. Nutrient cycling intensified, with guano-rich soils anchoring ecosystems. Heard’s volcanic activity intermittently reshaped its surface, creating ash-rich habitats that supported pioneering plant communities.
Technology & Material Culture
Globally, this was the era of Upper Paleolithic florescence: composite tools, bone harpoons, and artistic traditions from Lascaux to the Levant. None reached the Southeast Indian Ocean. Survival here would have demanded advanced maritime craft and cold-weather technologies, beyond the known reach of Paleolithic seafarers.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
Marine life moved along the circumpolar current, linking the subregion to Antarctica and Australasia. Whales traced seasonal migrations, while seabirds covered extraordinary distances, knitting together distant ecosystems. These biological corridors laid ecological foundations for later human exploitation of the Southern Ocean.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
No symbolic or cultural activity is tied to these islands. Elsewhere, symbolic traditions exploded: figurines, cave art, and ritual landscapes. The Southeast Indian Ocean remained beyond the human mental map, a space unknown yet ecologically rich.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Plant and animal communities adapted to dramatic climatic shifts—retreating glaciers, rising seas, and fluctuating volcanic activity. Recolonization after ice retreat showcased resilience, as mosses, lichens, and seabird-driven nutrient webs rapidly expanded into new niches.
Transition
By 7,822 BCE, the Ice Age was waning. The Southeast Indian Ocean islands stood transformed: glaciers reduced, coasts reshaped, ecosystems rebounding. Though still unseen by humans, they embodied subantarctic resilience at the cusp of the Holocene.
Southwest Indian Ocean (28,577–7,822 BCE): From Glacial Dominance to Holocene Beginnings
Geographic & Environmental Context
The subregion of Southwest Indian Ocean includes Kerguelen west of 70°E, the Îsles Crozet, Prince Edward Island, and Marion Island. Western Kerguelen’s ice-carved plateaus, the rugged volcanic Crozet peaks, and the smaller Prince Edward and Marion Islands defined this scattered maritime landscape.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
At the epoch’s start, glaciers dominated highlands across Kerguelen and the Crozets. By the Holocene transition, ice had retreated considerably, exposing valleys, coasts, and fertile volcanic soils. Sea levels rose globally, redrawing shorelines and submerging land bridges. Winds remained fierce, but slightly warmer temperatures lengthened ice-free seasons. The Southern Ocean’s productivity shifted with changing currents, supporting immense marine populations.
Subsistence & Settlement
Still unpeopled, the islands thrived ecologically. Vegetation expanded onto newly deglaciated slopes—mosses, lichens, and grasses colonized volcanic soils enriched by seabird guano. Seals, penguins, and albatrosses grew in numbers as ice-free coasts multiplied. Whales continued to feed in surrounding waters, making the subregion a biological hotspot.
Technology & Material Culture
Globally, Upper Paleolithic humans refined tools, ornaments, and symbolic practices, yet no trace of such material culture touched these isolated islands. Their inaccessibility underscored the limits of human seafaring in the Pleistocene.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current and westerly winds shaped ecosystems and migration. Birds nested across multiple island groups, creating interlinked ecological arcs. Whales moved along predictable feeding circuits. These corridors later drew human whalers and explorers, though in this epoch they remained exclusively natural.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
The subregion carried no human symbolic imprint. Instead, its symbolic resonance lay only in the ecological patterns—rookeries as centers of renewal, volcanic peaks as markers of resilience—beyond human perception at the time.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Ecosystems reorganized dynamically as ice retreated. Vegetation colonized bare rock, seabird populations redistributed, and marine mammals adapted to shifting ice margins. The resilience of life in this harsh zone foreshadowed ecological strategies that would continue into the Holocene.
Transition
By 7,822 BCE, the glacial epoch was ending. The Southwest Indian Ocean islands emerged into a new climatic regime—still remote, storm-battered, and uninhabited, yet ecologically flourishing. They stood as silent reservoirs of life at the dawn of a warmer age.
Northeastern Eurasia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Late Pleistocene–Early Holocene — Beringian Migrations, Salmon Economies, and the First Pottery Traditions
Geographic & Environmental Context
At the end of the Ice Age, Northeastern Eurasia—stretching from the Urals to the Pacific Rim—was a vast, deglaciating world of river corridors, boreal forests, and emerging coasts. It included three key cultural–ecological spheres:
-
Northwest Asia — the Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei heartlands, Altai piedmont lakes, and Minusinsk Basin, bounded by the Ural Mountains to the west. Here, deglaciation produced pluvial lake systems, and forest belts climbed into the Altai foothills.
-
East Europe — from the Dnieper–Don steppe–forest margins to the Upper Volga–Oka and Pripet wetlands, a corridor of interlinked rivers and pluvial basins supporting rich postglacial foraging.
-
Northeast Asia — the Amur and Ussuri basins, the Sea of Okhotsk littoral, Sakhalin and the Kuril–Hokkaidō arc, Kamchatka, and the Chukchi Peninsula—a maritime–riverine realm where early Holocene foragers developed salmon economies and pottery traditions under the warming Pacific westerlies.
Together these subregions formed a continuous arc of adaptation spanning tundra, taiga, and coast—an evolutionary laboratory for the technologies and traditions that would later circle the entire North Pacific.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød (14,700–12,900 BCE): Rapid warming and higher precipitation expanded boreal forests and intensified riverine productivity across Eurasia’s north. Salmon runs strengthened in the Amur and Okhotsk drainages; pluvial lakes filled the Altai basins.
-
Younger Dryas (12,900–11,700 BCE): A temporary cold–dry reversal restored steppe and tundra, constraining forests to valleys; lake levels fell; inland mobility increased.
-
Early Holocene (after 11,700 BCE): Stable warmth and sustained moisture drove forest advance (pine, larch, birch) and high lake stands; sea levels rose along the Okhotsk and Bering coasts, flooding older plains and establishing modern shorelines.
These oscillations forged adaptable forager systems able to pivot between large-game mobility and aquatic specialization.
Subsistence & Settlement
Across the northern tier, lifeways diversified and semi-sedentism began to take root:
-
Northwest Asia:
Elk, reindeer, beaver, and fish formed broad-spectrum diets. Lakeside camps in the Altai and Minusinsk basins became seasonal home bases, while Ob–Yenisei channels hosted canoe or raft mobility. Forest nuts and berries expanded plant food options in warm phases. -
East Europe:
Along the Dnieper, Don, and Upper Volga, foragers targeted elk, red deer, horse, and beaver, exploiting riverine fish and waterfowl. Repeated occupations at lake outlets and confluences reflect increasing site permanence and food storage. -
Northeast Asia:
The Amur–Okhotsk region pioneered salmon-based economies, anchoring early Holocene villages at river confluences and estuarine terraces. Coasts provided seal, shellfish, seabirds, and seaweeds, while inland foragers pursued elk and musk deer. Winter sea-ice hunting alternated with summer canoe travel along the Sakhalin–Kuril–Hokkaidō chain.
This mosaic of economies—lake fishers, river hunters, and sealers—reflected the continent’s growing ecological diversity.
Technology & Material Culture
Innovation was continuous and regionally distinctive:
-
Microblade technology persisted across all subregions, with refined hafting systems for composite projectiles.
-
Bone and antler harpoons, toggling points, and gorges evolved for intensive fishing and sealing.
-
Ground-stone adzes and chisels appeared, enabling woodworking and boat construction.
-
Early pottery, first along the Lower Amur and Ussuri basins (c. 15,000–13,000 BCE), spread across the Russian Far East—among the world’s earliest ceramic traditions—used for boiling fish, storing oils, and processing nuts.
-
Slate knives and grindstones at Okhotsk and Amur sites show specialized craft economies.
-
Personal ornaments in amber, shell, and ivory continued, while sewing kits with eyed needles and sinew thread supported tailored, waterproof clothing.
These toolkits established the technological template for later northern and Pacific Rim foragers.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Ob–Irtysh–Yenisei river systems funneled movement north–south, linking the steppe with the taiga and tundra.
-
Altai and Ural passes maintained east–west contact with Central Asia and Europe.
-
Dnieper–Volga–Oka networks merged the European forest-steppe into the greater Eurasian exchange field.
-
In the Far East, the Amur–Sungari–Zeya–Okhotsk corridor unified interior and coast, while the Sakhalin–Kuril–Hokkaidō arc allowed short-hop voyaging.
-
Across the Bering Strait, fluctuating sea levels intermittently connected Chukotka and Alaska, maintaining Beringian gene flow and cultural exchange.
These conduits supported both biological and technological diffusion at a continental scale.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ochre burials with ornamented clothing and ivory or antler goods reflect deep symbolic continuity from the Upper Paleolithic.
-
Petroglyphs and engravings in the Altai and Minusinsk basins, and later in Kamchatka, depict large animals, waterbirds, and solar motifs.
-
Amur basin figurines and carved marine-mammal and fish effigies attest to ritualized relationships with food species.
-
In the Far East, early evidence of first-salmon and bear-rite traditions foreshadows later Ainu and Okhotsk ceremonialism.
Across all subregions, water and game remained the core of spirituality, connecting people to cyclical abundance and ancestral landscapes.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Foragers across Northeastern Eurasia met environmental volatility with creative versatility:
-
Zonal mobility (taiga–tundra–coast) and multi-season storage (dried meat, smoked fish, rendered oils) stabilized food supply.
-
Boat and ice technologies extended reach across seasons.
-
Broad-spectrum diets cushioned against climatic downturns.
-
Flexible dwellings and social alliances allowed fission and fusion as resources shifted.
-
Memory landscapes—engraved rocks, ritual mounds, named rivers—preserved continuity through spatial change.
Genetic and Linguistic Legacy
The Beringian population standstill during the Late Glacial created a deep ancestral pool for both Paleo-Inuit and First American lineages, while reciprocal migration reconnected Chukchi, Kamchatkan, and Amur populations after sea-level rise.
These long-lived networks seeded circum-Pacific cultural parallels in salmon ritual, dog-traction, maritime hunting, and composite toolkits, forming the northern backbone of later trans-Pacific cultural continuity.
Long-Term Significance
By 7,822 BCE, Northeastern Eurasia had become one of the world’s great centers of forager innovation:
-
Northwest Asia’s pluvial lakes fostered early semi-sedentism and the first rock art of Siberia.
-
East Europe’s river–lake foragers stabilized broad-spectrum economies bridging steppe and forest.
-
Northeast Asia’s salmon-rich coasts and early pottery traditions created the technological and ritual matrix that would radiate across the North Pacific.
This continental synthesis of aquatic resource mastery, ceramic innovation, and long-range mobility defined the emerging Holocene north—a zone where people and landscape adapted together through water, ice, and memory.
Northeast Asia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper Paleolithic II — Beringian Standstill, Early Pottery Horizons, and Salmon Towns
Geographic and Environmental Context
Northeast Asia includes eastern Siberia east of the Lena River to the Pacific, the Russian Far East (excluding the southern Primorsky/Vladivostok corner), northern Hokkaidō (above its southwestern peninsula), and extreme northeastern Heilongjiang.
-
Anchors: the Lower/Middle Amur and Ussuri basins, the Sea of Okhotsk littoral (Sakhalin, Kurils), Kamchatka, the Chukchi Peninsula (with Wrangel Island offshore), northern Hokkaidō, and seasonally emergent shelves along the Bering Sea and northwest Pacific.
Climatic Crisis and Population Transformation During the LGM
Between roughly 28,500 and 20,000 years ago, the onset of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) profoundly altered Northeast Asia. Ice sheets, permafrost expansion, and ecological fragmentation reduced habitable zones across Siberia.
During and immediately after this period, the Ancient North Siberians were largely replaced by populations carrying ancestry closely related to East Asians. This was not a simple migration but a prolonged process of demographic turnover, admixture, and regional extinction.
Out of this transformation emerged two closely related populations:
-
Ancestral Native Americans
-
Ancient Paleosiberians (AP)
Paleoclimatic modeling strongly supports southeastern Beringia as a long-term refugium during the LGM, providing a stable ecological zone where these populations could persist, interact, and differentiate.
Climate and Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød (c. 14,700–12,900 BCE): warming and moisture increase expanded boreal forest into valleys; salmon runs intensified; nearshore productivity rose.
-
Younger Dryas (c. 12,900–11,700 BCE): brief return to cooler, drier conditions; tundra patches expanded but ice-free coasts still offered reliable marine resources.
-
Early Holocene (after c. 11,700 BCE): stabilizing warmth and rising sea level reshaped shorelines; taiga expanded fully; rich riverine and estuarine habitats matured.
Subsistence and Settlement
-
Deglaciating coasts supported seal and salmon economies; intertidal shellfish beds and seabird rookeries fueled seasonal aggregation.
-
In warming phases, diets diversified toward fish (salmon, sturgeon), small game, and plant foods (nuts, roots, berries).
-
Younger Dryas prompted higher mobility and renewed emphasis on large herbivores where herds persisted.
-
Early Holocene villages favored river confluences and coastal terraces, ideal for salmon weirs and broad foraging radii.
Technology and Material Culture
-
Microblade production refined; hafted composite points standardized for hunting and sealing.
-
Bone/antler harpoons with toggling tips; barbed fishhooks; sewing kits for tailored garments and waterproof seams.
-
Early pottery appears in the Lower Amur–Russian Far East and spreads to surrounding basins—among the world’s earliest ceramic traditions—used for fish oils, stews, and nut processing.
-
Ground-stone adzes for wood-working and dugout canoe manufacture; slate knives on some Okhotsk coasts.
Movement and Interaction Corridors
-
Amur–Sungari waterway integrated interior and coast; Sakhalin–Kuril–Hokkaidō island chain enabled short-hop voyaging.
-
Beringian standstill: populations on both sides of the strait developed long-term ties; fluctuating sea levels modulated contact.
-
Seasonal sea-ice bridges facilitated winter travel; summer lanes favored canoe movement.
Cultural and Symbolic Expressions
-
Carved bone and ivory figurines, zoomorphic engravings, and ochre burials persisted, signaling continuity with earlier Upper Paleolithic symbolic systems.
-
Recurrent salmon first-catch rites and bear/sea-mammal treatment practices are inferred from patterned discard and ritualized processing locales.
Environmental Adaptation and Resilience
-
Zonal mobility (taiga–tundra–coast) and storage (dried fish, rendered oils) buffered climate swings across Bølling–Allerød → Younger Dryas → Early Holocene.
-
Canoe technologies, fish weirs, and shoreline mapping (capes, tide rips, haul-outs) underwrote stable subsistence as forests spread and shorelines shifted.
Genetic and Linguistic Legacy
-
Prolonged Beringian population structure during late glacial–early Holocene times contributed ancestry to Paleo-Inuit and to the First Americans; reciprocal gene flow linked Chukchi–Kamchatka–Amur families.
-
These deep ties foreshadowed later circum-North Pacific cultural continuities in salmon ritual, dog-traction, and composite toolkits.
Transition Toward the Holocene Forager Horizons
By 7,822 BCE, Northeast Asia featured mature taiga coasts, prolific salmon rivers, and early pottery villages—a landscape primed for the broad-spectrum, semi-sedentary foraging economies that would dominate the Early Holocene and eventually feed into Epi-Jōmon/Satsumon, Okhotsk, and Amur basin cultural florescences.
Northern North America (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper Pleistocene II → Early Holocene — Deglaciation, Kelp Highways, and Pluvial Heartlands
Geographic & Environmental Context
From the Bering Strait and Aleutians to the Gulf of Alaska, down the Inside Passage–Haida Gwaii–Vancouver Island chain and along the Klamath–Redwood coast, and across the continent through the Yukon–Fraser–Columbia–Mississippi drainages to the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence, Hudson Bay, and the Mid-Atlantic–New England shore, Northern North America took shape as ice withdrew and seas rose.
Three interlocking spheres structured lifeways:
-
Northwestern North America — The Cordilleran–Beringian gateway, with Brooks Range and North Slopetundras, Yukon–Kuskokwim and Copper–Cook Inlet basins, the Gulf of Alaska and Aleutian arcs, and the Southeast Alaska–Haida Gwaii–outer BC fjordlands. Late-opening ice-free corridors and a sheltering, resource-rich kelp-forest coast defined movement and subsistence.
-
Gulf & Western North America — The California Current coast (Channel Islands to Puget/Salish), the Lower Mississippi and Gulf Coast estuaries, the Southern Plains, Colorado Plateau, and the Great Basin of pluvial lakes. Here, estuary chains, canyon springs, and inland basins created a patchwork of productive niches.
-
Northeastern North America — The Chesapeake–Delaware–Hudson–Gulf of Maine margins, Great Lakes–Ohio–Mississippi valleys, Appalachian ridge-and-valley, Upper St. Lawrence–Quebec, and the Baffin–Labrador rim. As the Ancylus/Champlain seas waxed and waned and isostatic rebound re-shaped coastlines, mixed forest–water ecotones proliferated.
Across all three spheres, postglacial estuaries, high-latitude tundra–taiga mosaics, and greening loess plainscreated an integrated coast–river–lake system that drew people into longer stays at dependable water-edge nodes.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød (c. 14.7–12.9 ka): Warmer, wetter conditions greened interior loess plains, invigorated riverine and lacustrine productivity, and stabilized nearshore kelp forests; small ice-free coastal pockets opened along the Gulf of Alaska and SE Alaska–BC fjords.
-
Younger Dryas (c. 12.9–11.7 ka): A sharp cold–dry pulse renewed steppe/tundra, pinched interior water sources, and funneled people to fjord mouths, estuaries, and spring-fed refugia where marine and riparian resources remained reliable.
-
Early Holocene (post-11.7 ka): Rapid warming and rising seas flooded outer shelves, forming the modern estuaries and sounds; oak–hazel–elm forests raced poleward; salmon-bearing rivers stabilized; Great Basinlakes still dotted the interior though retreating.
This cadence favored dual mobility—coast ↔ interior, lake ↔ plain—while encouraging semisedentary anchoring at rich aquatic nodes.
Subsistence & Settlement
A continent-spanning broad-spectrum foraging economy matured, increasingly underwritten by fisheries and wetland yields:
-
Northwestern Coast & Beringia: Foragers moved fjord by fjord along a “kelp highway,” harvesting rockfish, salmon, shellfish, sea urchins, waterfowl, and seals, with dugout/skin boats, tailored parkas, and sinew-sealed seams enabling year-round littoral rounds. Interior camps on river benches and rock shelters targeted caribou, elk, and whitefish/salmon at crossings; by the Early Holocene, weirs and fish traps appear, and stays on raised marine terraces lengthened toward semisedentism.
-
Gulf & Western Interior: Along the Lower Mississippi and Gulf estuaries, semirecurrent camps clustered on natural levees, working oyster bars, mullet/menhaden runs, and back-swamp fauna. On the California–Channel Islands and outer coast, dense shell-middens, canoe/raft use, and targeted seabird/sea-mammalharvests foreshadow later maritime societies. In the Great Basin and Southwest, shore camps on pluvial lakescaptured fish and waterfowl, while pronghorn and small-game drives, geophyte digging, and seed processing rounded out diets.
-
Northeast & Great Lakes: Estuary and bay-head hamlets on the Severn–Delaware–Hudson–Maine coasts built early shell heaps; interior Great Lakes–river communities fished salmonids and sturgeon, hunted deer and moose, and gathered hazelnut, oak mast, and berries. Camps were seasonal but repeatedly reoccupied on dune ridges and terrace knolls, laying down deep middens and cemeteries.
Across all zones, semisedentary seasonality—anchoring at rich nodes with radiating forays—became a hallmark of the period.
Technology & Material Culture
Light, adaptable, and increasingly specialized toolkits supported both mobility and storage:
-
Lithics: Persistent microblade industries in the NW; widespread backed bladelets, trapezes, and notched/side-notched points elsewhere.
-
Aquatic gear: Bone/antler harpoons (often toggling), gorges, barbed points; stake-weirs, woven fish baskets, and net floats/sinkers; dugouts and skin boats on protected waters.
-
Processing & containers: Grinding slabs and handstones for seeds/geophytes; drying racks and smokehouses for fish/meat; organic containers (bark, skin); early use of blubber oils for waterproofing gear.
-
Ornaments & pigments: Beads of shell, bone, jet/amber, and teeth; ochre widely used in body/ritual contexts; carved bone/antler animal motifs signal deepening predator–prey cosmologies.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
A web of redundant routes ensured resilience:
-
Coastal: stepwise Southeast Alaska–Haida Gwaii–Vancouver Island–Puget; Klamath–Channel Islands arcs; short-hop cabotage between estuaries.
-
Riverine: Yukon, Fraser, Columbia, Sacramento–San Joaquin, Mississippi–Ohio–Illinois, St. Lawrence—all served as driftways, trade channels, and seasonal migration guides.
-
Overland: Drakensberg-style highland corridors in the Rockies and Appalachians; portages binding watersheds; interior Great Plains and boreal routes linking basins.
These corridors moved not only people and tools but also dried fish, fat, hides, pigments, and ideas, knitting together far-flung bands.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
Symbolic life was entwined with water, animals, and place:
-
Rock art and pecked engravings mark canyon walls and coastal shelters; imagery of salmon, seals, caribou, bear, and watercraft points to a cosmology of reciprocity with “animal persons.”
-
Red-ochre burials with curated toolkits and ornaments cluster near estuaries, lake margins, and river terraces, fixing lineage rights to critical nodes.
-
Midden mounds and lacustrine deposits served as ceremonial foci and archives of feast and return, materializing ancestral claims over weirs, groves, and crossings.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Forager strategies balanced anchoring with agility:
-
Coastal–interior duality ensured protein continuity through climatic pulses;
-
Storage of oils, dried fish/meat, and nuts underwrote winter and drought survival;
-
Fine-grained seasonal scheduling tracked flood pulses, salmon runs, waterfowl migrations, and mast years;
-
Territorial norms around weirs, springs, and beaches managed access and minimized conflict.
These practices allowed populations to ride out the Younger Dryas setback and capitalize on Early Holocene productivity.
Long-Term Significance
By 7,822 BCE, Northern North America had coalesced into a storage-rich, water-anchored forager world: salmon estuaries and kelp-forest coasts in the northwest, pluvial-lake and estuary chains across the west and Gulf, and forest–river–bay mosaics in the northeast.
This emergent system—portfolio subsistence, semi-sedentary nodes with radiating rounds, engineered fisheries and food storage, and ritualized tenure over key waters—formed the durable substrate from which later Northwest Coast maritime societies, Archaic mound-building traditions, and riverine trade networks would grow as the Holocene unfolded.
The earliest evidence for human presence in North America emerges during this period, though the timing and routes of initial migration remain subjects of intense scientific debate. Human footprints preserved in ancient lake sediments at White Sands, New Mexico, provide the strongest evidence for human activity around 21,000-23,000 years ago, placing people in North America during the height of the Last Glacial Maximum.
These early inhabitants likely arrived via two possible routes: coastal migration along the Pacific Northwest using watercraft to navigate ice-free shorelines, or overland passage through Beringia—the vast land bridge connecting Siberia to Alaska when sea levels dropped due to massive continental ice sheets. Archaeological evidence of coastal occupation from this period would now lie submerged beneath 100 meters of post-glacial sea level rise.
During the Last Glacial Maximum (26,500-19,000 years ago), much of northern North America remained locked under ice sheets, but Beringia provided a viable refuge where humans could have lived alongside now-extinct megafauna including woolly mammoths, horses, and giant ground sloths. Some controversial sites suggest even earlier human presence—potentially 26,000-30,000 years ago—though these claims await broader scientific acceptance.
As the climate gradually warmed after 19,000 years ago, retreating ice sheets began opening new migration corridors and habitable territories. Small, highly mobile bands of hunter-gatherers adapted to diverse environments from tundra grasslands to emerging forests, setting the stage for the more widespread continental occupation that would follow.
Northwestern North America (28,577 – 7,822 BCE) Upper Paleolithic II — Deglaciation Gateways, Coastal Pathways, and Inland Refugia
Geographic and Environmental Context
Northwestern North America includes Alaska, western Canada (Alberta, British Columbia, Yukon and Northwest territory and Nunavut west of 110°W) Alaska, Washington State, northern Idaho, and the northwestern portions of Montana, Oregon, and California.
Anchors: the Bering Strait & Seward Peninsula, Brooks Range & North Slope, Yukon–Kuskokwim and Copper–Cook Inlet basins, the Gulf of Alaska & Aleutians, the Inside Passage/Haida Gwaii and outer coast of British Columbia, the Stikine–Skeena–Fraser–Columbia plateaus and canyons, Puget Sound, and the Klamath–Redwood coast of NW California.
-
Deglaciation opened seasonal lanes between the Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets late; the Pacific fjord coast developed rich estuaries; interior loess plains greened.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Bølling–Allerød warming (c. 14,700–12,900 BCE) improved forage and river productivity; Younger Dryas (c. 12,900–11,700 BCE) briefly re-invigorated cold, aridity; Early Holocene warmth followed.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Coastal “kelp highway” foragers harvested kelp-forest fish, shellfish, sea mammals, and seabirds along the Gulf of Alaska–BC archipelagos.
-
Inland, caribou and elk dominated mesas and river crossings; fish (salmon, whitefish) took on growing importance with weirs and traps by the Early Holocene.
-
Camps proliferated on raised marine terraces, river benches, and rock shelters.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Persistent microblade technology; bone harpoons, barbed points; early dugout precursors for nearshore travel.
-
Tailored parkas and waterproof seams (sinew thread, blubber oil dressings) support maritime rounds.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Fjord-by-fjord voyaging stitched Southeast Alaska–Haida Gwaii–Vancouver Island; inland river driftways (Yukon, Upper Fraser) linked plateaus.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Red-ochre burials and curated toolkits suggest emergent territorial memory; carved bone/antler animal imagery reflects predator–prey relations.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Dual-mobility strategy (coast and interior) ensured redundancy across climatic pulses; seasonal storage of dried fish/oils began to anchor semi-sedentism.
Transition
By 7,822 BCE, salmon estuaries and deglaciated coasts enabled increasingly fish-centered economies while inland big-game pursuits persisted.
Recent archaeological discoveries suggest humans may have reached North America significantly earlier than the traditional 'Clovis First' model of 13,000-14,000 years ago. Well-documented footprints at White Sands, New Mexico, confirmed by multiple independent dating methods, place human presence at 21,000-23,000 years ago. More controversial sites suggest even earlier dates, though these claims remain highly disputed among scholars."
Polynesia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Late Pleistocene–Early Holocene Transition — Emerging Arcs, Drowned Plateaus, and Reef Foundations
Geographic & Environmental Context
During the Late Pleistocene and early Holocene, Polynesia—stretching from the Hawaiian archipelago across Samoa, Tonga, the Cook and Society Islands, to the far eastern outliers of Pitcairn and Rapa Nui—remained entirely unpeopled, a scattered constellation of volcanic and reefed islands rising above the world’s largest ocean.
At the Last Glacial Maximum (c. 26,500–19,000 BCE), global sea levels stood more than 100 m lower than today, exposing wide coastal shelves and tightening inter-island channels. As ice sheets melted, deglaciation flooded ancient shorelines, transforming basins into lagoons and seamounts into isolated atolls.
-
North Polynesia (Oʻahu, Maui Nui, Kauaʻi–Niʻihau, Midway Atoll): the Maui Nui shelf—once a single island—became a cluster of channels; Midway’s rim expanded as new lagoons formed.
-
West Polynesia (Hawaiʻi Island, Tonga, Samoa, Tuvalu–Tokelau, Cook, Society, and Marquesas): reefs and barrier lagoons built up around volcanic peaks, while low atolls appeared as sea level rose.
-
East Polynesia (Pitcairn, Rapa Nui, and nearby seamounts): the farthest outposts of the Pacific, geologically young and ecologically self-contained, fringed by narrow reef flats and rich upwelling zones.
Across this immense realm, oceanic currents—the South and North Equatorial and the Kuroshio–Equatorial Counter-flow system—created predictable gyres, establishing the hydrological backbone that would later sustain Polynesian voyaging.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
The epoch was one of oscillation and renewal:
-
Last Glacial Maximum (26,500–19,000 BCE): cooler seas and exposed shelves expanded coastal plains; coral growth slowed under lowered sea level.
-
Bølling–Allerød interstadial (c. 14,700–12,900 BCE): warmth and rainfall increased; reefs surged upward in “catch-up” growth; lagoons and barrier formations matured.
-
Younger Dryas (12,900–11,700 BCE): brief cooling flattened reef accretion and restricted mangroves; trade-wind aridity spread in leeward belts.
-
Early Holocene (after 11,700 BCE): steady warming and sea-level stabilization allowed coral terraces, mangroves, and strand forests to reach near-modern equilibrium.
By 7822 BCE, the Pacific climate engine had achieved its Holocene rhythm—warm, humid, and oceanically stable.
Biota & Baseline Ecology (No Human Presence)
Polynesia’s ecosystems reached pristine balance under rising seas:
-
Reefs and lagoons flourished with coral, mollusks, crustaceans, and reef fish (parrotfish, surgeonfish, mullet); spur-and-groove structures and back-reef ponds became marine nurseries.
-
Coastal vegetation—pandanus, beach heliotrope, ironwood, and grasses—rooted in guano-enriched sands; strand forests stabilized dunes.
-
Cloud-forests cloaked high islands such as Tahiti and Savaiʻi, while dry leeward slopes supported shrub and palm mosaics.
-
Seabirds nested in immense colonies; turtles hauled out on beaches; marine mammals frequented newly formed bays.
All existed in predator-free isolation, each island a laboratory of speciation and resilience.
Geomorphic & Oceanic Processes
As the sea rose, island landscapes underwent continuous re-sculpting:
-
Reef accretion kept pace with transgression, forming the first true atoll rings.
-
Maui Nui’s plateau fragmented into separate islands; Hawaiʻi Island’s volcanic plains met new coasts.
-
Eastern high islands (Rapa Nui, Pitcairn) gained fertile volcanic soils through slow weathering; storm surges and wave reworking created terraces and embayments.
-
Sediment deltas at stream mouths formed early estuarine wetlands—future sites for Polynesian fishponds and irrigated terraces.
Symbolic & Conceptual Role
For millennia these lands remained beyond the human horizon—unimagined yet forming the ecological architecture that would one day welcome voyagers. Their mountains, lagoons, and reefs became the stage on which later Polynesian societies would enact origin stories of sea and sky.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
Natural resilience was inherent:
-
Coral reefs tracked rising seas through vertical growth, preventing ecological collapse.
-
Guano-fertilized soils accelerated vegetative colonization after storm disturbance.
-
Cloud-forest hydrology maintained water flow even in drier pulses.
These feedbacks produced long-term equilibrium between land, sea, and atmosphere—the defining ecological rhythm of Polynesia.
Long-Term Significance
By 7,822 BCE, Polynesia had become a fully modern oceanic system: drowned plateaus transformed into lagoons and atolls; coral terraces and forest belts stabilized; seabird and reef ecologies reached peak diversity.
Though still empty of humankind, the region now possessed every element—predictable currents, fertile reefs, sheltered bays, and stable climates—that would, tens of millennia later, make it the natural cradle of the world’s greatest voyaging tradition.