Southeast Europe (909 BCE – 819 CE): …
Years: 909BCE - 819
Southeast Europe (909 BCE – 819 CE): Iron Kingdoms, Roman Frontiers, and Byzantine Beginnings
Regional Overview
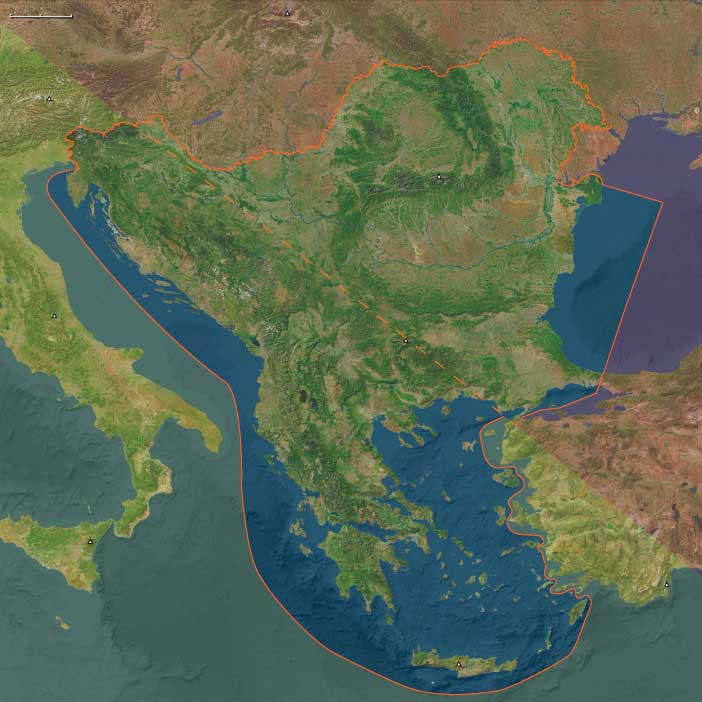
Between the Adriatic and the Black Sea, Southeast Europe stood for a millennium as the hinge between the Mediterranean world and the steppe.
Its twin landscapes—the eastern Danubian–Thracian plains and the western Adriatic–Illyrian mountains—produced parallel yet intertwined histories.
Both absorbed Hellenic colonization, entered the Roman orbit, and later weathered the migrations that forged medieval Europe.
The region’s story from the early Iron Age to late Antiquity is thus one of fusion and frontier, where Greek, Roman, Thracian, Illyrian, and Slavic worlds met and reshaped one another.
Geography and Environment
The region divides naturally:
-
Eastern Southeast Europe embraces the Lower Danube, Thracian plain, and Black Sea coast, enclosed by the Balkan and Carpathian arcs. Fertile lowlands sustained dense agrarian settlement, while the Danube served as both artery and barrier.
-
Western Southeast Europe rises into karstic uplands and Adriatic coasts, with sheltered island chains and mountain basins suited to mixed farming and seaborne trade.
Climatic variation—humid along the coasts, continental inland—produced complementary economies: grain, salt, and metals from the east; timber, livestock, and maritime goods from the west.
Seasonal river floods and Adriatic storms shaped transport calendars; alpine passes and sea lanes linked every valley to the wider Mediterranean.
Societies and Political Developments
Greek Colonies and Indigenous Kingdoms
From the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, Greek settlers established poleis along both coasts: Apollonia and Dyrrhachium on the Adriatic; Odessos, Mesambria, and Histria on the Black Sea.
Behind them, Illyrian, Thracian, and Geto-Dacian tribes forged early kingdoms—the Odrysian realm in Thrace, the Ardiaean and Dardanian dominions in the west.
These polities traded metals, grain, and slaves for imported wine, oil, and ceramics, mediating between the Mediterranean and the interior.
Rome and the Imperial Frontier
Between the 2nd century BCE and the 1st century CE, Rome absorbed the entire peninsula: Macedonia, Illyricum, Dalmatia, Moesia, Thrace, and briefly Dacia north of the Danube.
Roman roads—the Via Egnatia, Via Militaris, and Sava-Drava corridors—stitched the provinces together.
Urban centers such as Salona, Skupi, Nicomedia, and Serdica reflected Roman law and architecture, while legionary camps and bridgeheads (Apollodorus’ bridge at Drobeta) turned the Danube into the empire’s longest fortified line.
Mining in Dacia, shipyards on the Adriatic, and grain estates in Moesia underpinned prosperity until the 3rd-century crises.
Migrations and the Byzantine Transition
From the 3rd to 7th centuries CE, the frontier dissolved under waves of Goths, Huns, Avars, and Slavs.
Cities were sacked, repopulated, and repurposed as Byzantine forts.
The Eastern Roman Empire, centered on Constantinople, re-emerged as the stabilizing power, holding Thrace and the coastal Adriatic while fostering Christianization.
By the late 7th century, the First Bulgarian Empire rose in Moesia and Thrace; Croatian and Serbian principalities took form in the western mountains, bridging the late antique and medieval orders.
Economy and Exchange
Agriculture remained the foundation:
-
The Thracian plain and Wallachian lowlands exported grain and livestock along the Danube.
-
The Adriatic coasts specialized in wine, oil, salted fish, and amphora industries.
-
Mining of gold, silver, and iron in Dacia and the western ranges enriched both local chieftains and Roman prefects.
Trade routes—riverine, overland, and maritime—made the region a corridor between the Aegean, the Pannonian plain, and the steppe.
After Rome’s decline, Byzantine and Bulgar administrations preserved key arteries, ensuring continuity of commerce despite political fragmentation.
Technology and Material Culture
Iron metallurgy and Roman engineering reshaped daily life.
Stone bridges, aqueducts, and bath complexes signaled urban sophistication; rural estates used the iron plow to expand cultivation.
Local craftsmanship persisted: Thracian and Illyrian metalwork, Dacian goldsmithing, and later Slavic wood and textile arts.
Christian churches and monasteries, often rising atop pagan sanctuaries, announced new spiritual geographies while reusing classical masonry.
Belief and Symbolism
Religious life reflected the region’s pluralism:
-
Indigenous cults—Zalmoxis, the Thracian Horseman—coexisted with Greek polytheism and Roman state worship.
-
Christianity spread from urban bishoprics by the 4th century CE, producing early saints and councils.
-
Slavic and Bulgar paganisms, with sky- and ancestor-deities, persisted until conversion in the 8th–9th centuries.
Thus the region became a spiritual palimpsest, each new faith overlaying rather than erasing the old.
Adaptation and Resilience
Southeast Europe’s resilience lay in its geographical layering: river corridors, mountain refuges, and island coasts offered fallback zones in war or climate stress.
Agro-pastoral economies allowed mobility; fortified towns and hillforts provided refuge during invasions.
Byzantine fiscal systems and Bulgar tribute networks recycled Roman infrastructures, ensuring survival of settlement and trade patterns despite continual upheaval.
Regional Synthesis and Long-Term Significance
By 819 CE, Southeast Europe had completed its ancient cycle.
In the east, Byzantine Thrace and the Bulgar kingdom defined a Christian–steppe frontier along the Danube.
In the west, Slavic kingdoms grew amid the ruins of Roman Dalmatia, while the Adriatic cities preserved classical urbanism under imperial and papal influence.
Greek colonies, Roman provinces, and barbarian migrations had fused into a single cultural continuum—one that naturally divides into eastern (Danubian–Thracian) and western (Adriatic–Illyrian) spheres yet remains bound by geography, trade, and faith.
This equilibrium of coast and hinterland, empire and tribe, set the pattern for the medieval Balkans: a region perpetually contested but never peripheral, mediating between the Mediterranean world and the steppes beyond.
Groups
- Polytheism (“paganism”)
- Roman Empire: Tetrarchy
- Christianity, Arian
- Hungarian people
- Roman Empire: Constantinian dynasty (Nicomedia)
- Roman Empire: Constantinian dynasty (Constantinople)
- Slavs, South
- Christianity, Chalcedonian
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Leonid dynasty
- Avars, Eurasian
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Justinian dynasty
- Avar Khaganate (Eurasian Avars)
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Heraclian dynasty
- Bulgarian Empire (First)
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Heraclian dynasty
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Isaurian dynasty
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Nikephorian dynasty
- Roman Empire, Eastern: Non-dynastic
Topics
Commodoties
- Domestic animals
- Oils, gums, resins, and waxes
- Grains and produce
- Textiles
- Ceramics
- Salt
- Sweeteners
- Beer, wine, and spirits