North Polynesia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper …
Years: 28577BCE - 7822BCE
North Polynesia (28,577 – 7,822 BCE): Upper Paleolithic II — Deglaciation, Rising Seas, and Reef Terraces
Geographic & Environmental Context
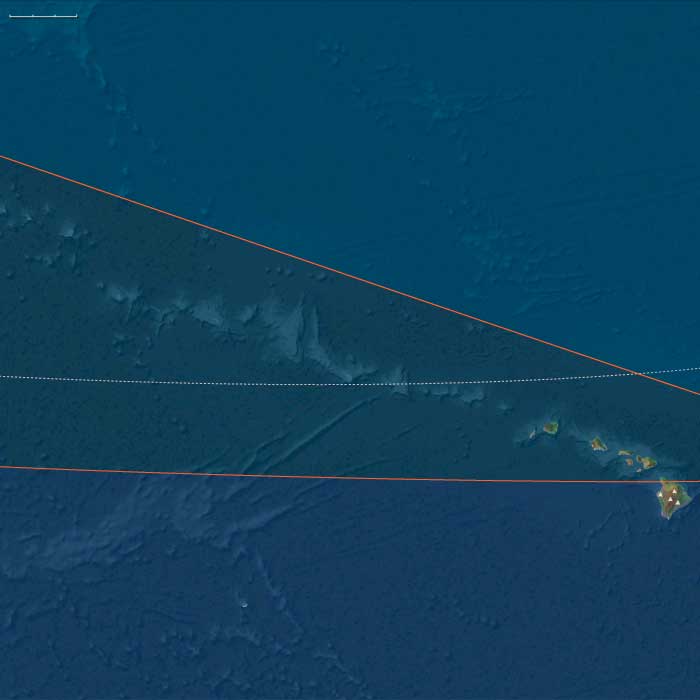
North Polynesia includes the Hawaiian Islands chain except Hawaiʻi Island (the Big Island) — principally Oʻahu, Maui, Kauaʻi, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Niʻihau — plus Midway Atoll.
-
Anchors: Windward Oʻahu reef benches; Maui Nui’s now-flooding inter-island shelf (tightening channels between Maui–Molokaʻi–Lānaʻi); Kauaʻi–Niʻihau cliff coasts; Midway’s expanding lagoon rim.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Deglaciation lifted sea level >100 m, drowning paleo-shorelines and pushing reefs landward into new terraces and embayments.
-
Bølling–Allerød warming then Younger Dryas snapback produced stepwise reef catch-up; Early Holocenewarmth stabilized growth.
Biota & Baseline Ecology (No Human Presence)
-
Reef accretion built coral terraces and spur-and-groove formations; nearshore lagoons teemed with parrotfish, surgeonfish, and mullet.
-
Seabird nutrient inputs (guano) enriched dune vegetation; coastal strand forests established on emerging sand spits.
Long-Term Significance
The migrating shoreline created productive lagoons and sheltered landings—future hubs for waʻa (canoe) anchorages and fishpond siting.