East Micronesia (909 BCE – 819 CE): …
Years: 909BCE - 819
East Micronesia (909 BCE – 819 CE): Post-Settlement Flourishing — Maneaba Houses, Stick-Chart Knowledge, and High-Island Specialization
Geographic & Environmental Context
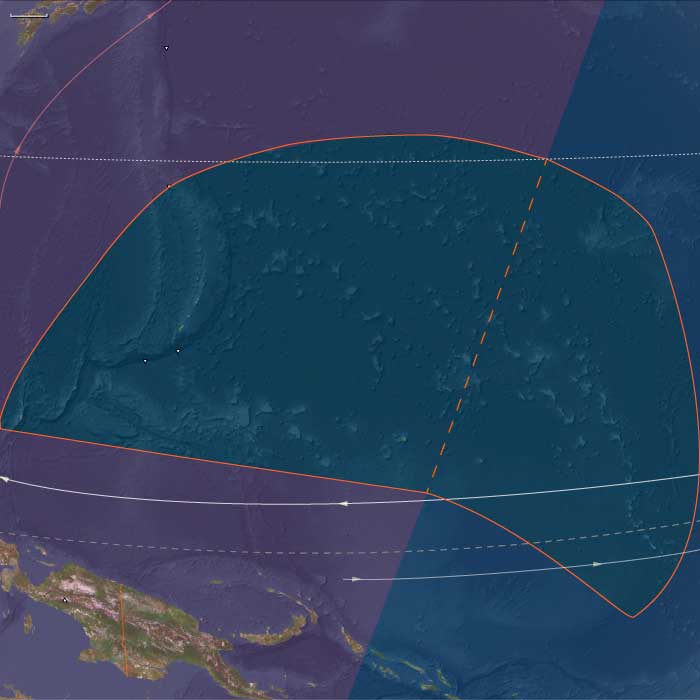
East Melanesia includes Kiribati (Gilbert Islands), the Marshall Islands (Ralik and Ratak chains), Nauru (uplifted phosphatic limestone island), and Kosrae (high, volcanic island on the eastern Caroline arc).
-
Anchors: Ralik–Ratak villages (Marshall Islands), Gilbert atoll districts (Kiribati), Nauru’s plateau villages, and Kosrae’s stream-fed valleys and sheltered reef.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
First-millennium oscillations increased ENSO drought risk on equatorial atolls; Kosrae’s streams and orographic rains buffered shortages; intra-chain redistribution grew in importance.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Atolls: intensified taro-pit agriculture; seasonal breadfruit surplus dried into bwiro (fermented paste); coconut toddy and pandanus paste diversified diet.
-
Kosrae: wet-field taro systems developed in stream valleys; basalt adze workshops began to supply regional demand.
-
Nauru: small lens-fed gardens and reef fisheries sustained modest populations.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Canoe fleets standardized (outriggers with crab-claw sails); refined voyaging guilds transmitted star compasses and swell-reading;
-
Stick charts crystallized into Marshallese rebbelib (overall) and meddo (localized) mnemonic maps; shell and bone fishhooks diversified; fine fiber mats and sennit cordage proliferated.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Regular Ralik–Ratak tribute and reciprocity circuits; Gilbert chain north–south canoe lanes; Kosrae served as a high-island hub for freshwater, timber, and basalt adzes; San Andrés/Caroline sphere to the west remained an external partner.
Belief & Symbolism
-
Maneaba (Kiribati meeting house) traditions formed as political–ritual centers; navigators held sacred knowledge and ritual obligations; ancestor shrines guarded wells and groves.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Distributed islet zoning and inter-atoll reciprocity buffered drought and storm damage; food preservation(dried breadfruit, pandanus paste, smoked fish) extended security; canoe logistics ensured rapid relief within chains.
Transition
By 819 CE, East Micronesia had matured into a lattice of atoll chiefdoms and a high-island node (Kosrae), bound by canoe routes, maneaba institutions, and stick-chart navigation — a resilient oceanic system poised for the monumental phase (e.g., Lelu) of the later medieval centuries covered in our 1108–1251 and 1252–1395 narratives.