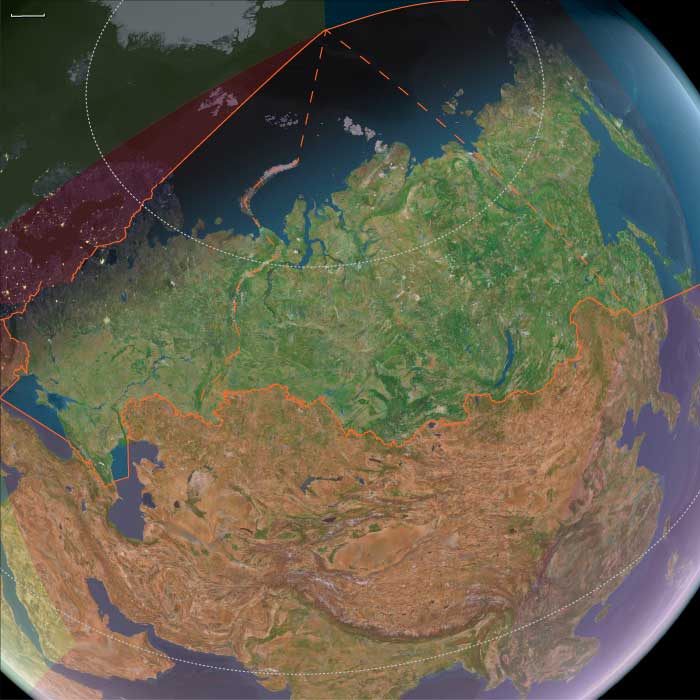
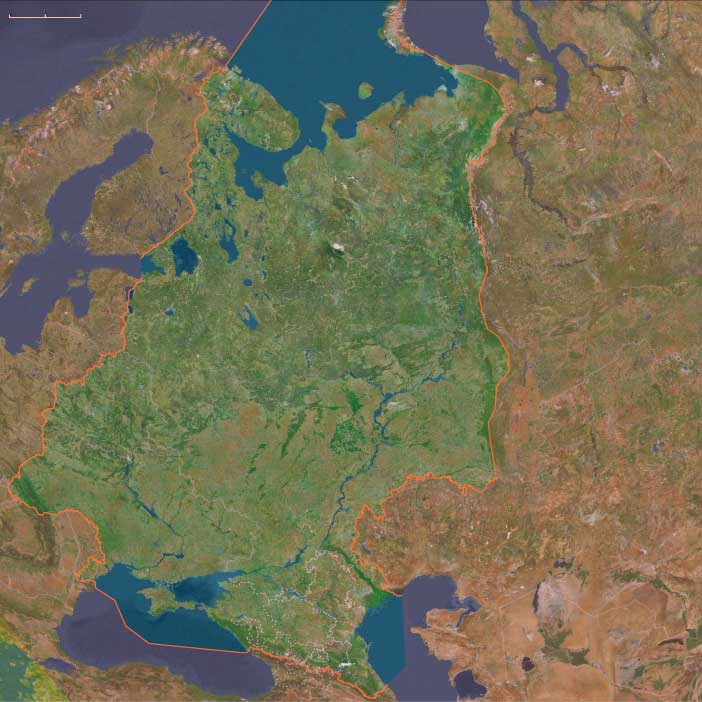
East Europe (1732–1743 CE): Expansion and Internal …
Years: 1732 - 1743
East Europe (1732–1743 CE): Expansion and Internal Consolidation
Political and Military Developments
Continued Imperial Expansion
Between 1732 and 1743 CE, Russia continued its territorial and imperial ambitions, further solidifying control over newly acquired regions. The period saw significant political efforts to integrate these territories effectively into the expanding empire.
Strengthening Central Administration
The Russian government enhanced centralization, reinforcing administrative reforms to improve efficiency and ensure effective governance across extensive and diverse territories.
Diplomatic Strategy and Alliances
Russia further strengthened its international presence through strategic diplomacy, maintaining alliances, and engaging actively in European political affairs. This strategy reinforced Russia’s geopolitical influence and maintained regional stability.
Economic and Technological Developments
Economic Expansion and Industrial Progress
Economic conditions continued to improve significantly, driven by industrial expansion in sectors like mining, manufacturing, and agriculture. Enhanced trade networks further facilitated sustained economic growth.
Infrastructure Improvements
Infrastructure saw ongoing improvements, particularly in transportation and urban development. Roads, canals, and public buildings benefited from continued investments, promoting economic activity and administrative effectiveness.
Cultural and Artistic Developments
Flourishing Cultural Patronage
Cultural development continued vigorously, supported by sustained patronage from the Russian elite. Architectural, artistic, and literary works thrived, reflecting increased European influences and enriching Russia’s cultural landscape.
Intellectual and Educational Growth
Intellectual activities expanded further, with educational institutions proliferating and scholars actively engaging with contemporary European thought. Continued literary and academic production enriched Russia's intellectual tradition.
Settlement Patterns and Urban Development
Urban Expansion and Development
Urban areas, especially Moscow and Saint Petersburg, experienced ongoing growth and development. Urban planning improvements, infrastructure advancements, and public amenities enhanced urban life, economic vitality, and administrative coherence.
Enhanced Defense Infrastructure
Ongoing enhancements in urban and territorial fortifications remained essential, reinforcing security and protecting urban centers and strategic locations from potential threats.
Social and Religious Developments
Social Cohesion and Integration
Social reforms and integration policies continued to develop, further incorporating diverse ethnic and regional groups into the fabric of Russian society, enhancing societal stability and administrative efficiency.
State-Church Relations
The relationship between the state and the Orthodox Church evolved further, with reforms continuing to align religious practices with state goals. These adjustments reshaped the church's societal role, ensuring its continued integration within the broader imperial framework.
Long-Term Consequences and Historical Significance
The period from 1732 to 1743 CE marked continued territorial expansion, administrative strengthening, and cultural enrichment. These developments solidified Russia's status as a powerful European empire and laid essential foundations for its future growth and international prominence.
People
Groups
- Christians, Eastern Orthodox
- Sweden, (second) Kingdom of
- Denmark-Norway, Kingdom of
- Russia, Tsardom of
- Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (Commonwealth of the Two Nations)