Central Europe (1252–1395 CE): Dynastic Crowns, Mining …
Years: 1252 - 1395
Central Europe (1252–1395 CE): Dynastic Crowns, Mining Economies, and Alpine Confederations
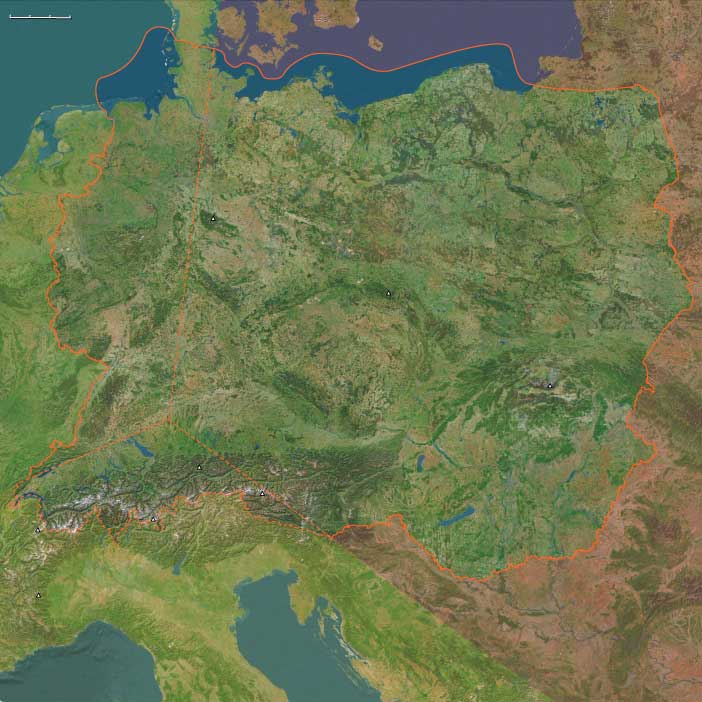
Between the Vistula and the Rhine, from the Carpathian passes to the Alpine lakes, Central Europe in the Lower Late Medieval Age entered a period of consolidation, reform, and urban ascent. The age’s empires and kingdoms—the Luxembourgs of Bohemia, the Angevins and early Jagiellons in Hungary and Poland, and the emergent Habsburgs on the Danube—combined dynastic ambition with pragmatic governance. Mining booms, expanding universities, and the spread of urban leagues drew this vast inland heart of the continent into closer alignment with the Mediterranean and Baltic worlds.
In the east and north, the Kingdom of Bohemia, under the Přemyslid and later Luxembourg dynasties, became an imperial powerhouse. Ottokar II (r. 1253–1278) extended Bohemian rule across Austria and Styria before falling at Marchfeld to Rudolf of Habsburg. A generation later, the Luxembourgs transformed Prague into the political and cultural capital of the Holy Roman Empire. Charles IV (r. 1346–1378), King of Bohemia and Holy Roman Emperor, issued the Golden Bull of 1356, defined the imperial electors, founded Charles University (1348), and raised Prague’s Gothic skyline with the Charles Bridge and St. Vitus Cathedral. Prosperity flowed from Kutná Hora’s silver mines, whose revenues funded coinage, civic works, and imperial patronage.
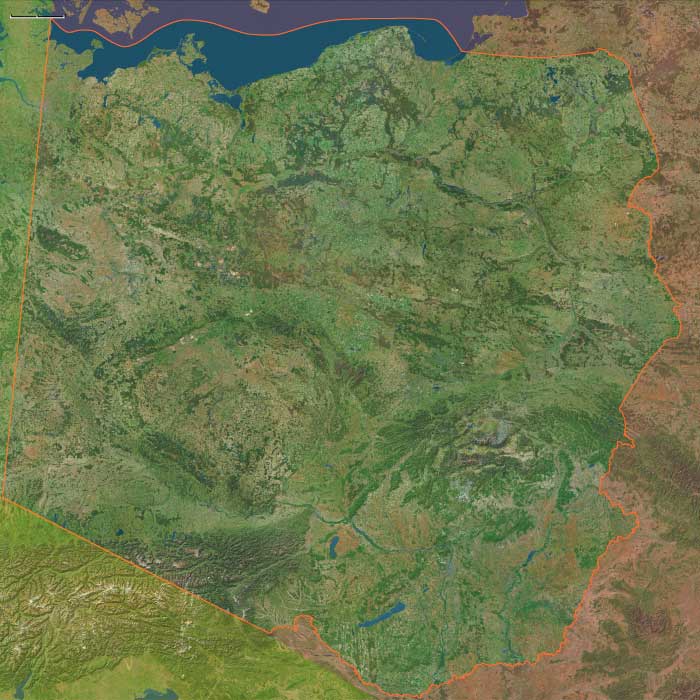
To the east, Poland, long fragmented among regional dukes, was reunited under Władysław I Łokietek in 1320 and reached maturity under Casimir III “the Great” (r. 1333–1370). His reforms of law and administration, his founding of Kraków University (1364), and his incorporation of Red Ruthenia restored the kingdom’s authority. Following Casimir’s death, the Polish crown passed in personal union to Louis I of Hungary, and after his reign the Union of Krewo (1385) joined Poland and Lithuania under Jogaila (as Władysław II Jagiełło) and Queen Jadwiga, forging the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth’s earliest foundations.
Hungary, meanwhile, rose again under the Angevin line. Charles I (1308–1342) and Louis I “the Great” (1342–1382) reasserted royal power after the decline of the Árpáds, exploiting rich mineral wealth in Kremnica, Rudabánya, and Upper Hungary (modern Slovakia). Gold florins struck at the Kremnica mint circulated across Europe. Mining towns under German law flourished in the Carpathian uplands, and new roads over the Transylvanian passes carried salt, livestock, and silver north toward Kraków. After 1387, Sigismund of Luxembourg ascended Hungary’s throne, binding it dynastically to Bohemia and the Empire.
Along the Danube, the Habsburgs consolidated their Austrian heartland after 1278, making Vienna both a market city and an intellectual center—its university founded in 1365. Across Germany’s eastern marches, the Golden Bull enshrined the electors of Mainz, Trier, Cologne, Bohemia, Brandenburg, Saxony, and the Palatinate, stabilizing imperial governance. Brandenburg, passing from Ascanian to Wittelsbach and then to Luxembourg control, began its slow ascent under the margraves of the late fourteenth century. Urban prosperity followed river networks: the Elbe, Oder, and Vistula bound inland markets to the Hanseatic League ports on the Baltic.
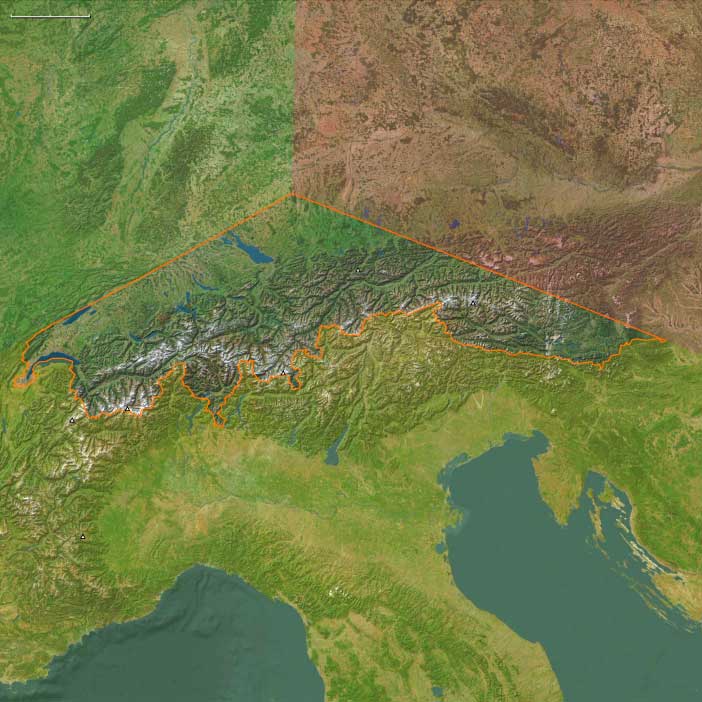
Farther south, East Central Europe blended into the Alpine and Danubian core. The Swiss Confederation, born of rural leagues at Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden (1291), defended its autonomy against Habsburg encroachment at Morgarten (1315). Over the next century, alliances of towns and valleys—Lucerne, Zürich, Bern, and Glarus—coalesced into the early Eidgenossenschaft. To the east, leagues in Graubünden such as the Grey League (late 14th c.) coordinated defense and toll control across the Alpine passes.
The southern corridors—Gotthard, Splügen, St. Bernard, and Brenner—carried Lombard cloth and spices north and sent Alpine wool, hides, and cheese south. Merchant guilds operated fortified warehouses and toll stations, and fairs in Zurich, Chur, and along the Rhine–Bodensee system linked the Alpine world to Frankfurt and the Hanseatic ports. Despite recurrent feuds, city militias and confederate alliances kept trade open, transforming the once-peripheral uplands into Europe’s vital north–south hinge.
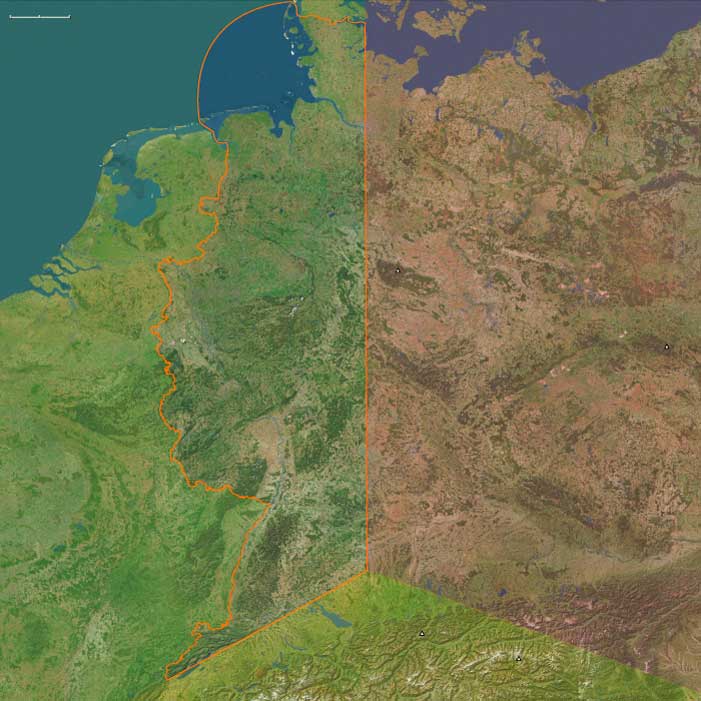
In West Central Europe, the Rhine–Main heartland thrived on commerce and ecclesiastical wealth. The Golden Bull of 1356 confirmed Mainz, Trier, and Cologne as prince-electors, cementing the political geography of the Empire. Frankfurt, midway between the Alps and the North Sea, hosted the imperial fairs where Italian bankers met Flemish clothiers and Hanseatic merchants. The Rhine wine trade prospered even under cooler Little Ice Age conditions; vintners adapted vineyards along the Moselle and Rheingau to changing climates.
Cathedral cities—Cologne, Worms, Speyer, Mainz, and Basel—dominated both devotion and diplomacy. Their Gothic towers embodied civic pride as well as spiritual renewal. The Black Death (1348–1352) devastated towns, sparking flagellant processions and persecution of Jewish communities in the Rhine cities, but urban guilds soon recovered, consolidating political voice. Basel, rebuilt after its 1356 earthquake, became a bridge between the Empire and the Swiss Confederation, both commercially and intellectually.
Technological and institutional innovations strengthened recovery throughout Central Europe. The spread of the three-field system, heavy ploughs, and watermills improved yields; water-powered pumps and adit drainage revolutionized mining. Civic law—Magdeburg and Lübeck codes—standardized administration from Kraków to Vienna. Universities in Prague, Kraków, and Vienna formed a northern constellation of learning where scholasticism, Roman law, and natural philosophy converged.
The region’s resilience rested on its networks. When plague or war closed overland routes, merchants shifted to the Vistula and Danube, or joined Hanseatic convoys at the Baltic. Dynastic marriages and elective compromises balanced fragmentation with unity: Luxembourgs linked Bohemia, Hungary, and the Empire; Habsburgs and Angevins wove Austria and Hungary together; and the Jagiellonian alliance bridged Poland and Lithuania. Through mining wealth, market towns, and learning, Central Europe forged institutions strong enough to withstand crisis and to shape the continent’s next age.
By 1395 CE, Central Europe had matured into a dense fabric of crowns and communes. Prague glittered as the imperial capital of the Luxembourgs; Kraków anchored a Polish–Lithuanian union; Buda and Vienna stood astride the Danube as twin centers of royal power; and the Swiss Confederates guarded their Alpine freedoms against princely overlords. The Rhine and Danube, the Vistula and Elbe, carried not only goods but the ideas and alliances that would soon ignite the Hussite reforms, Jagiellonian ascendancy, and Habsburg expansion—making Central Europe the decisive heart of the continent’s late medieval transformation.

East Central Europe (with civilization) ©2024-25 Electric Prism, Inc. All rights reserved.
People
- Casimir III the Great
- Charles I of Hungary
- Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
- Henry I
- Jadwiga of Poland
- Jogaila (Władysław II)
- Louis I of Hungary
- Ottokar II of Bohemia
- Rudolf I of Germany
- Sigismund
- Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia
- Wladyslaw I the Elbow-high
Groups
- Polytheism (“paganism”)
- Germans
- Hungarian people
- Wends, or Sorbs (West Slavs)
- Christianity, Chalcedonian
- Bavarians (West Germanic tribe)
- Thuringia, Duchy of
- Passau, Bishopric of
- Saxony, Duchy of
- Germany, Kingdom of (within the Holy Roman Empire)
- Holy Roman Empire
- Hanseatic league (informally organized)
- Slovaks (West Slavs)
- Carinthia, Duchy of
- Czechs [formerly Bohemians] (West Slavs)
- Hungary, Kingdom of
- Habsburg, House of
- Bamberg, Prince-Bishopric of
- Saxons, Transylvanian
- Poland, Greater
- Poland during the period of fragmentation, Kingdom of
- Mazovia, Duchy of
- Austria, Archduchy of
- Brandenburg (Ascanian) Margravate of
- Bohemia, Kingdom of
- Mecklenburg, House of
- Bavaria, Wittelsbach Duchy of
- Styria, Duchy of
- Anhalt, Principality of
- Ordensstaat (Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights)
- Lübeck, Free City of
- Brunswick-Lüneburg, Duchy of
- Regensburg (Ratisbon), Imperial Free City of
- Cammin, Prince-Bishopric of
- Anhalt-Bernburg, Principality of
- Anhalt-Aschersleben, Principality of
- Anhalt-Zerbst, Principality of
- Holy Roman Empire
- Bavaria, Upper, Duchy of
- Bavaria, Lower, Duchy of
- Galicia–Volhynia, Kingdom of
- Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Duchy of
- Salzburg, Archbishopric of
- Saxe-Wittenberg, Duchy of
- Saxe-Ratzeburg-Lauenburg, Duchy of
- Saxe-Mölln-Bergedorf, Duchy of
- Teutonic Knights of Prussia, or Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights (House of the Hospitalers of Saint Mary of the Teutons in Jerusalem)
- Poland of the later Piasts, Kingdom of
- Brandenburg, Wittelsbach
- Bavaria, Wittelsbach Duchy of
- Lithuania, Grand Duchy of
- Mecklenburg, Duchy of
- Bavaria-Straubing, Wittelsbach Duchy of
- Bavaria-Landshut, Wittelsbach Duchy of
- Saxony, Electorate of
- Brandenburg, (Luxembourg) Margravate of
- Poland of the Jagiellonians, Kingdom of
- Lithuania, Grand Duchy of
- Bavaria-Munich, Wittelsbach Duchy of
- Bavaria-Ingolstadt, Wittelsbach Duchy of
Topics
- Ostsiedlung (German: Settlement in the East), a.k.a. German eastward expansion
- Poland, Fragmentation of
- Western Architecture: 1252 to 1396
- Marchfeld, Battle of
- Black Death, or Great Plague