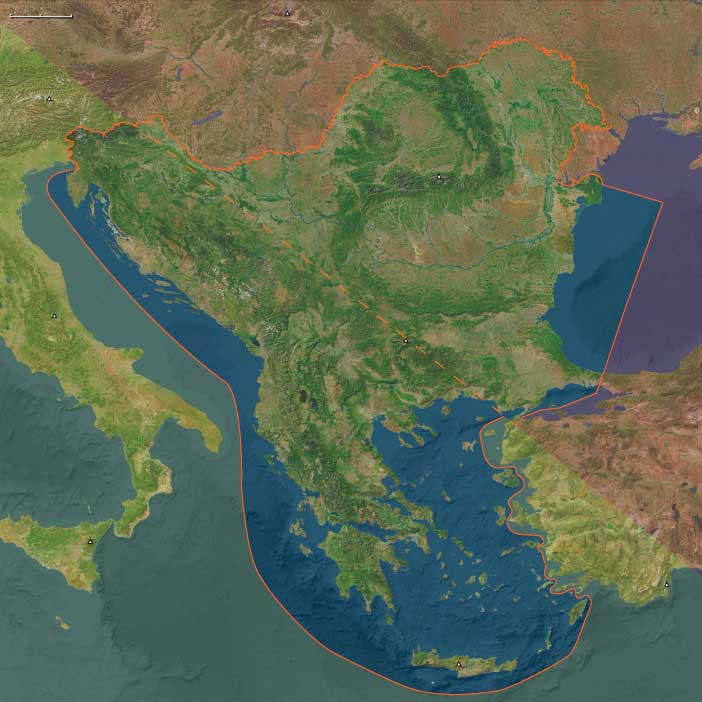
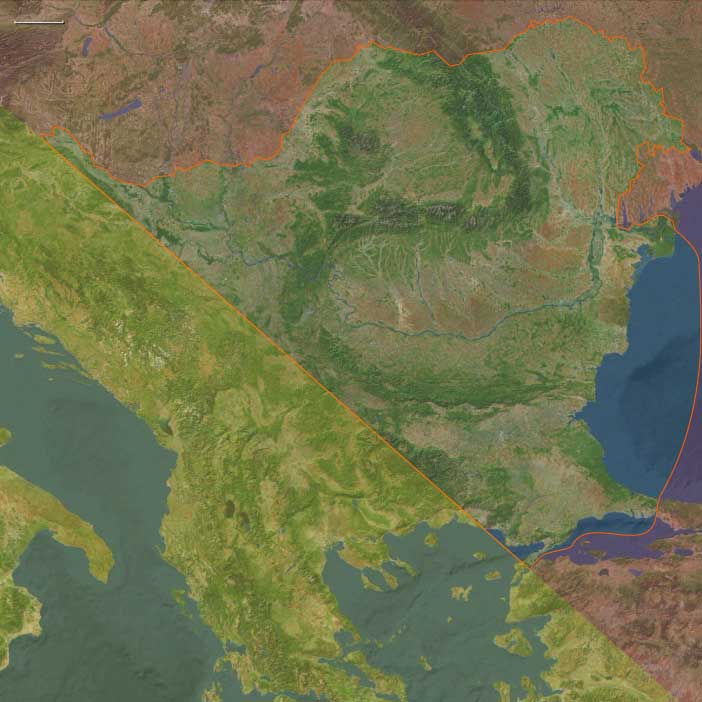
The long-term effects of the Plague of …
Years: 544 - 555
As the disease spreads to port cities around the Mediterranean, the struggling Goths are reinvigorated and their conflict with Constantinople enters a new phase.
The plague weakens the Empire at a critical point, when Justinian's armies have nearly retaken all of Italy and the western Mediterranean coast; the evolving conquest would have reunited the core of the Western Roman Empire with the Eastern Roman Empire.
Although the conquest occurs in 554, the reunification will not last long.
In 568, the Lombards will invade Northern Italy, defeat the small imperial army that had been left behind, and establish the Kingdom of the Lombards.
The plague may have also contributed to the success of the Arabs a few generations later in the Byzantine-Arab Wars.
Locations
People
Groups
Topics
Subjects
Regions
Subregions
Related Events
Filter results
Showing 10 events out of 57704 total
Several revolts against Chinese rule in the period between the beginning of the Six Dynasties to the end of the Tang Dynasty take place in the region of present Vietnam, such as those of Ly Bon and his general and heir Trieu Quang Phuc; and those of Mai Thúc Loan and Phùng Hung.
All of them ultimately fail, yet most notable are Ly Bon and Trieu Quang Phuc, whose Anterior Ly Dynasty will rule for almost half a century, from 544 to 602, before the Chinese Sui Dynasty reconquers their kingdom, Van Xuan.
The Six Dynasties is a collective term for six Chinese dynasties in China during the periods of the Three Kingdoms, Jin dynasty, and Southern and Northern Dynasties.
East Central Europe (544–555 CE): Lombard Ascendancy, Battle of Asfeld, Gepid Weakening, and Early Byzantine-Avar Diplomacy
Between 544 and 555 CE, East Central Europe—encompassing Poland, Czechia, Slovakia, Hungary, and those portions of Germany and Austria lying east of 10°E and north of a line stretching from roughly 48.2°N at 10°E southeastward to the Austro-Slovenian border near 46.7°N, 15.4°E—underwent significant geopolitical shifts, primarily characterized by Lombard territorial expansion and the corresponding weakening of the Gepid kingdom. Under King Audoin (546–560 CE), the Lombards expanded their influence significantly, culminating in their decisive victory at the Battle of Asfeld (552 CE). This defeat severely weakened the Gepids under King Thurisind, although the Gepids retained limited control of their eastern territories, primarily in modern-day eastern Hungary and Transylvania. Concurrently, the Byzantine Empire actively engaged in diplomatic efforts, skillfully balancing regional rivalries to secure its northern frontier. Near the close of this era (around 558–562 CE), the first arrival of the Pannonian Avars from Central Asia near the Danube further complicated regional dynamics, as Byzantium began forming initial alliances with them.
Political and Military Developments
-
Lombard territorial expansion under King Audoin reached a peak in 552 CE with the Lombard victory at the Battle of Asfeld, significantly reducing Gepid military strength and territorial integrity.
-
Gepids, though greatly weakened, maintained limited regional authority eastward in Transylvania, under continued pressure from Lombard aggression.
-
Byzantine diplomacy actively balanced alliances, supporting the Lombards strategically to prevent Gepid resurgence while simultaneously preparing for the emergence of the newly arriving Avars.
Economic and Cultural Developments
-
Economic stability persisted across Lombard territories, characterized by vibrant agricultural communities, robust livestock economies, and stable trade routes linking settlements such as Augusta Vindelicorum (Augsburg), Vindobona, and Aquincum.
-
Lombard cultural expressions flourished, blending Germanic traditions with Byzantine influences in their metalwork, pottery, and decorative arts.
Slavic Expansion and Consolidation
-
The clearly differentiated Slavic groups (Sclaveni, Antes, and West Slavic tribes like Polanes, Sorbs, Obotrites, Veleti, and White Croats) rapidly expanded into territories progressively vacated or weakened by Gepid setbacks, significantly increasing their demographic and cultural presence.
Long-Term Consequences
This era marked a turning point, setting the stage for greater geopolitical upheavals. The severe weakening of the Gepids following Asfeld (552 CE) created power vacuums soon exploited by incoming Avars and rapidly expanding Slavic populations, fundamentally reshaping East Central Europe's demographic and cultural landscape.
Slavic tribes have settled in Moravia and Bohemia along the valleys of the Moravia and upper Elbe Rivers by the first half of the sixth century.
Audoin is the founder of the Lombard dynasty that will crush the Gepidae, absorb the survivors into the Lombard nation, and establish Lombard power in the Italian peninsula, much of which it will rule for the next two centuries.
The Longobards, or Lombards, now Arian Christians, attack the Gepids on behalf of Justinian, who awards them with land in Pannonia and Noricum (modern Hungary and eastern Austria).
The foundation upon which the Eastern Roman Empire will rest for nearly a century is laid by Justinian, whose administrative reforms greatly advance the unification of the diverse peoples of the empire in a Hellenic context.
He wages almost constant warfare between 535 and 554 in the west.
Drawing his professional forces mostly from the Balkans, he greatly expands the empire's territory by conquering the southern Levant, northern Africa, and Italy, in an effort to recreate the domain of the old Roman Empire.
Justinian has driven the invaders from the Roman empire, but imperial defenses will prove inadequate to maintain this gain, and his institutional reforms will prove far more lasting than his military conquests.
Emperor Justinian, in addition to the long war he prosecutes against the Ostrogoths for control of Italy, wars repeatedly with the Sassanian Persians, but these eastern conflicts usually end with the Romans buying peace.
Justinian extorts heavy taxes from his subjects to finance his wars.
Eastern Southeast Europe (544–555 CE): Recovery, Reconquest, and Continuing Challenges
Settlement and Migration Patterns
Persistent Demographic Challenges
Between 544 and 555 CE, Eastern Southeast Europe continued grappling with lingering demographic challenges stemming from the Plague of Justinian. Although the initial devastation subsided, the region remained vulnerable due to reduced population levels, impacting both urban and rural settlements.
Slavic Migration
During this period, significant Slavic migrations reshaped the Balkan Peninsula's demographic composition. As Slavs established themselves throughout the region, these migrations significantly influenced settlement patterns and laid the groundwork for future demographic shifts.
Political and Military Developments
Justinian's Territorial Reconquests
Emperor Justinian's ambitious campaigns culminated in notable territorial reconquests, including Italy, Dalmatia, North Africa, and parts of Southern Hispania. The temporary reunification of these territories with the Eastern Roman Empire represented a brief revival of imperial unity and influence in the Mediterranean.
Continued Military Strain
Despite territorial gains, the empire remained under immense strain, both economically and militarily. The enduring impacts of the plague weakened imperial armies at a critical juncture, complicating further military and administrative consolidation efforts.
Economic and Technological Developments
Gradual Economic Stabilization
The regional economy began a cautious recovery, though ongoing agricultural disruptions and trade challenges persisted. Economic resilience slowly emerged as imperial policies adapted to the lingering impacts of the plague.
Infrastructure and Technological Maintenance
Significant attention remained on maintaining and enhancing infrastructure, particularly urban fortifications and key public works. Technological efforts focused on supporting military and economic resilience amid continued demographic and logistical challenges.
Cultural and Artistic Developments
Cultural Continuity and Adaptation
Cultural and artistic production reflected both continuity and adaptation during this challenging period. Continued development of Christian art and architecture symbolized resilience, providing societal cohesion and spiritual reassurance.
Preservation of Intellectual Heritage
Educational and scholarly institutions persevered, actively preserving classical and theological knowledge. Intellectual activities remained vigorous, adapting effectively to contemporary crises and societal disruptions.
Social and Religious Developments
Adaptive Governance and Resilience
Imperial administration continued to adapt to the ongoing crises, implementing policies aimed at economic recovery, demographic stabilization, and effective regional governance. These administrative adjustments were crucial in navigating the post-plague challenges.
Deepening Christian Influence
The role of Christianity further expanded, significantly shaping regional social, cultural, and political frameworks. The growing prominence of religious institutions helped bolster community resilience, providing essential moral and social support.
Long-Term Consequences and Historical Significance
The era from 544 to 555 CE marked a critical transitional period characterized by territorial reconquests, demographic adaptations, and gradual economic stabilization following the devastating plague. While Justinian's reunification efforts were notable, persistent vulnerabilities facilitated subsequent invasions, notably by the Lombards and later by Arab forces, shaping the region's historical trajectory profoundly.
Justinian has reconquered many former territories of the Western Roman Empire, including Italy, Dalmatia, Africa and Southern Hispania, but the Slavs occupy much of the Balkan Peninsula during his reign.
The Middle East: 544–555 CE
Strengthening States and Tribal Conflicts
Khosrau I: Consolidation of the Sassanid State
In the era from 544 to 555 CE, Persian ruler Khosrau I continues the legacy of his father, solidifying the authority of the Sassanid Empire following the suppression of the Mazdakite upheaval. His decisive actions ensure the dominance of orthodox Zoroastrianism—known as the Mazdean Church—across Persia. For his pivotal role in defeating Mazdakism and restoring stability, Khosrau earns the unique honorific title of Anosharvan, meaning "with the immortal soul," highlighting his contribution to strengthening both the state and its religious institutions.
Arab Tribal Warfare
During the same period, the Lakhmid kingdom, a client state of the Sassanid Persians based in southern Iraq, initiates vigorous military campaigns against Roman-controlled Syria and their rival client state, the Ghassanids. Despite their sustained efforts, the Lakhmids ultimately fail to achieve significant victories, and Roman Syria remains resilient under Ghassanid protection. These tribal conflicts illustrate the ongoing geopolitical rivalry between Persian and Roman spheres of influence, further complicating regional stability in the Middle East.
Thus, the years from 544 to 555 CE see both internal consolidation in Persia and continued friction among Arab vassal states, maintaining the delicate balance of power and setting the stage for further tensions in the region.