Andamanasia (7,821 – 6,094 BCE) Early …
Years: 7821BCE - 6094BCE
Andamanasia (7,821 – 6,094 BCE) Early Holocene — Canoe Villages, Sago Groves, and Reef Harvests
Geographic and Environmental Context
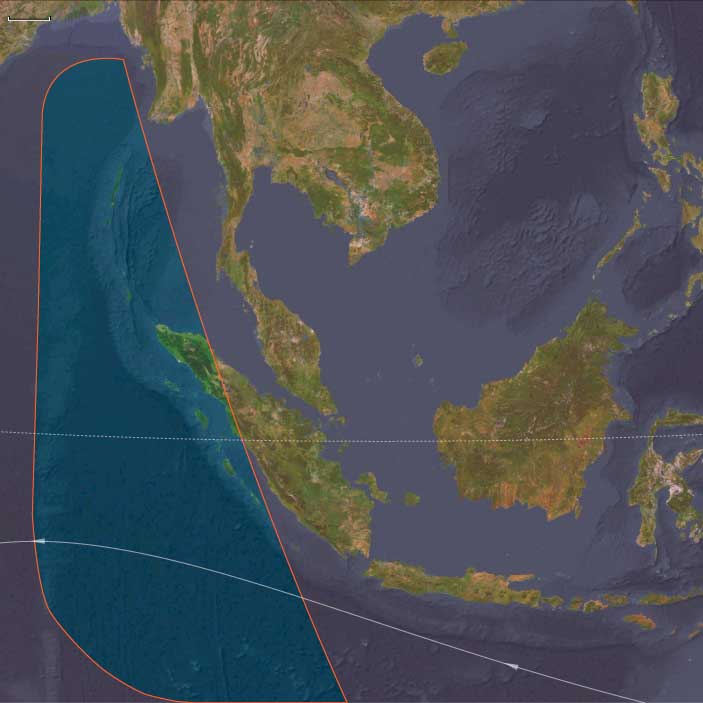
Andamanasia encompasses:
-
Andaman Islands (North, Middle, South Andaman) and Nicobar Islands.
-
Aceh in northern Sumatra, with nearby islands (Simeulue, Nias, Batu, Mentawai).
-
The Cocos (Keeling) Islands.
-
The Preparis, Coco, and Little Coco Islands (off Myanmar).
Anchors: North–South Andaman coasts and reefs, Nicobar Great Channel, Aceh’s Weh Island and Lhokseumawe–Banda Aceh corridor, Simeulue–Nias–Mentawai arc, Preparis/Coco islets, Cocos (Keeling) lagoon.
-
Andamans: lush rainforest belts; estuaries at river mouths.
-
Nicobars: mangrove channels, coconut palms, breadfruit groves.
-
Aceh/Nias: forested capes, tidal flats.
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Holocene optimum: warm, wet, productive reefs; monsoons stable.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Semi-sedentary canoe hamlets on Andamans/Nicobars; diets: pigs, deer, shellfish, turtle, fish, pandanus, coconut, sago.
-
Outer islands: subsistence on breadfruit, taro, reef fish.
-
Canoe traffic distributed goods, food, and kin links.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Ground-stone adzes, shell fishhooks, net weights; barkcloth; dugout canoes.
-
Early pottery may appear at Aceh’s coastal villages.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Island-hopping along the Nicobar–Andaman–Aceh arc; canoe convoys moved resin, shell, dried fish.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ancestor shrines near canoe landings; ritual feasts at turtle nesting seasons.
Environmental Adaptation & Resilience
-
Seasonal scheduling: turtle rookeries, sago harvest, yam patches buffered variability.
Transition
By 6,094 BCE, Andamanasia’s forager societies had canoe-linked resilience strategies.